Tetramer-blocking assay for defining antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes using peptide-MHC tetramer
- PMID: 16441426
- PMCID: PMC11159744
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00149.x
Tetramer-blocking assay for defining antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes using peptide-MHC tetramer
Abstract
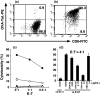
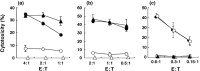
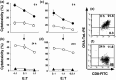
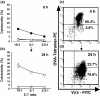
Peptide-MHC tetramers have been engineered to allow accurate detection of antigen-specific cytotoxic C lymphocytes (CTL) by flow cytometry. Here, we propose a novel use for peptide-MHC tetramers in the specific and sensitive analysis of the cytotoxic function of antigen-specific CTL by blocking MHC-restricted antigen-specific cytotoxicity. We found that pretreatment of ovalbumin (OVA)-specific CD8(+) CTL (OT-1 CTL), derived from OT-1 T-cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic mice, with OVA(257-264) peptide-H-2K(b) tetramer caused a marked inhibition of the cytotoxicity against OVA-expressing EG-7 tumor cells. OVA(257-264) peptide-H-2K(b) tetramer did not block the cytotoxicity mediated by 2C mouse (H-2(b))-derived CD8(+) CTL, which recognize allo (H-2L(d)) antigens. Moreover, OT-I CTL activity was not inhibited by an irrelevant HBV(208-216) peptide-H-2K(b) tetramer. These results indicate that the blocking of CTL activity with peptide-MHC tetramer was caused by interference with the interaction between the TCR and H-2K(b)-OVA(257-264) peptide complex, but not with the CD8-MHC class I interaction. The blocking activity of OVA(257-264) peptide-H-2K(b) tetramer was reversible because OT-I CTL pretreated with the tetramer recovered their cytotoxicity after culturing with interleukin-2 for 24 h. The same results were also demonstrated in freshly isolated, in vivo-primed OT-1 CTL sorted by the tetramer. These results demonstrate that peptide-MHC tetramer is a useful tool for defining MHC-restricted antigen-specific CTL function. Moreover, our finding implies that the measurement of CTL activity immediately after tetramer-guided sorting is not a suitable method for evaluating the function of in vivo-induced tetramer-positive CTL. We believe that the tetramer-blocking assay presented here will be useful for functionally monitor the induction of MHC-restricted antigen-specific CTL during vaccination therapy against tumor and infectious diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo augmentation of tumor-specific CTL responses by class I/peptide antigen complexes on microspheres (large multivalent immunogen).J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):228-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.228. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496404
-
Characterization of the Fas ligand/Fas-dependent apoptosis of antiretroviral, class I MHC tetramer-defined, CD8+ CTL by in vivo retrovirus-infected cells.J Immunol. 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2751-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2751. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11884442
-
Raising allo-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes by co-culture of murine splenocytes with autologous macrophage bearing the peptide/allo-major histococompatibility complex.Hum Immunol. 2009 Feb;70(2):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.11.005. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Hum Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19100802
-
Thymus-leukemia antigen (TL) as a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class Ib molecule and tumor-specific antigen.Cancer Sci. 2004 Jun;95(6):469-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03234.x. Cancer Sci. 2004. PMID: 15182425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of mouse models to better understand mechanisms of autoimmunity and tolerance.J Autoimmun. 2010 Nov;35(3):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jul 23. J Autoimmun. 2010. PMID: 20655706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptor 3 signal augments radiation-induced tumor growth retardation in a murine model.Cancer Sci. 2018 Apr;109(4):956-965. doi: 10.1111/cas.13543. Epub 2018 Mar 25. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29465830 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of apoB-100 Peptide-Specific CD8+ T Cells in Atherosclerosis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Jul 15;6(7):e005318. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005318. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28711866 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-oxidative Amino Acid L-ergothioneine Modulates the Tumor Microenvironment to Facilitate Adjuvant Vaccine Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 4;10:671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00671. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31019508 Free PMC article.
-
Combination immunotherapy with radiation and CpG-based tumor vaccination for the eradication of radio- and immuno-resistant lung carcinoma cells.Cancer Sci. 2009 May;100(5):934-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01114.x. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19245434 Free PMC article.
-
Dab2, a negative regulator of DC immunogenicity, is an attractive molecular target for DC-based immunotherapy.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Feb 3;4(1):e984550. doi: 10.4161/2162402X.2014.984550. eCollection 2015 Jan. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 25949867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howard MC, Spack EG, Choudhury K, Greten TF, Schneck JP. MHC‐based diagnostics and therapeutics − clinical applications for disease genes. Immunol Today 1999; 20: 161–5. - PubMed
-
- Altman JD, Moss PAH, Goulder PJR et al. Phenotypic analysis of antigen‐specific T lymphocytes. Science 1996; 274: 94–6. - PubMed
-
- Bousso P, Casrouge A, Altman JD et al. Individual variations in the murine T‐cell response to a specific peptide reflect variability in naïve repertoires. Immunity 1998; 9: 169–78. - PubMed
-
- Lee PP, Savage PA, Fong L et al. Characterization of circulating T cells specific for tumor‐associated antigens in melanoma patients. Nature Med 1999; 5: 677–85. - PubMed
-
- Yee C, Riddell SR, Greenberg PD. In vivo tracking of tumor‐specific T cells. Cur Opin Immmunol 2001; 13: 141–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

