Activation of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways by fibronectin requires integrin alphav-mediated ADAM activity in hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel functional target for gefitinib
- PMID: 16441427
- PMCID: PMC11159791
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00152.x
Activation of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways by fibronectin requires integrin alphav-mediated ADAM activity in hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel functional target for gefitinib
Erratum in
- Cancer Sci. 2006 Mar;97(3):242
Abstract
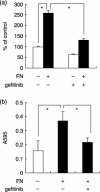
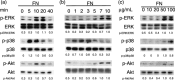
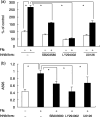
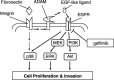
We have shown that the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839) inhibits the development of intrahepatic metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma CBO140C12, and EGFR transactivation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha is a possible target of gefitinib. In the present study, we focused on the fibronectin (FN)-dependent signaling pathway to further elucidate the antimetastatic activity of gefitinib in CBO140C12 cells. We initially observed that FN induced activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 and Akt, as well as cell proliferation and CBO140C12 cell invasion. These responses were mediated by EGFR tyrosine kinase, because gefitinib inhibited these effects of FN. FN-induced ERK, p38 and Akt activation was partly blocked by the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-pseudo-peptide FC-336, anti-alphav integrin antibody RMV-7, the broad-spectrum matrix metalloprotease inhibitor GM6001 and the broad spectrum a disintegrin and metalloprotease (ADAM) inhibitor TAPI-1. But these inhibitors had no effect on EGF-induced signaling pathways, suggesting that integrins and ADAM may be upstream components of EGFR in these responses. These results suggest that FN-induced activation of ERK, p38, Akt, cell proliferation and invasion was mediated, at least in part, via integrins, ADAM and EGFR, and that this FN-induced signaling pathway might be involved in the antimetastatic activity of gefitinib.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sensitivity to gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839) in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines correlates with dependence on the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and EGF receptor/Akt pathway for proliferation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Apr;3(4):465-72. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004. PMID: 15078990
-
Heregulin beta1 drives gefitinib-resistant growth and invasion in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2007;9(4):R50. doi: 10.1186/bcr1754. Breast Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17686159 Free PMC article.
-
Selective inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and metastatic activities by gefitinib.Br J Cancer. 2005 May 9;92(9):1690-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602548. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15841081 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms involved in PGE2-induced transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 11;31(1):72. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-72. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22967907 Free PMC article.
-
PLC and PI3K pathways are important in the inhibition of EGF-induced cell migration by gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839).Breast Cancer. 2004;11(4):367-73. doi: 10.1007/BF02968044. Breast Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15604992
Cited by
-
Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec 16;6(1):426. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00830-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34916490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different roles of integrin-β1 and integrin-αv for type IV secretion of CagA versus cell elongation phenotype and cell lifting by Helicobacter pylori.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Jul 21;16(7):e1008135. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008135. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32692784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Crosstalks in Liver Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2011 May 18;3(2):2444-61. doi: 10.3390/cancers3022444. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212818 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin-binding DNA aptamer treatment attenuates renal fibrosis under diabetic conditions.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 17;7(1):8490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09238-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28819200 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Conversations in Glioblastoma Progression, Diagnosis and Treatment.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):585-603. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01212-9. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35411434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, Normanno N. Epidermal growth factor‐related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 1995; 19: 183–232. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME. EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 2001; 37 (Suppl. 4): S9–S15. - PubMed
-
- Woodburn JR. The epidermal growth factor receptor and its inhibition in cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther 1999; 82: 241–50. - PubMed
-
- Khazaie K, Schirrmacher V, Lichtner RB. EGF receptor in neoplasia and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1993; 12: 255–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

