Fetal intestinal fibroblasts respond to insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II better than adult intestinal fibroblasts
- PMID: 16441878
- PMCID: PMC1382201
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-6-4
Fetal intestinal fibroblasts respond to insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II better than adult intestinal fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: We compared IGF responses of fetal and adult intestinal fibroblasts to identify a developmental difference in the IGF-axis. Intestinal fibroblasts were isolated from maternal and fetal jejunum. Media was conditioned at confluence and one week afterwards. The proliferative response at confluence to 5 nM IGF-I or -II was compared.
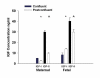
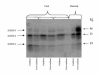
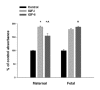
Results: There were no significant differences in IGFBP expression at confluence. Post-confluence, fetal fibroblasts had no significant changes in IGFBP-2 and IGFBP-3 expression. Post-confluent maternal fibroblasts had increased IGFBP-3 levels that were significant compared to the fetal fibroblasts. IGF-I increased in post-confluent fetal fibroblasts, while in maternal fibroblasts it decreased (p < 0.001). IGF-II secretion decreased significantly in post-confluent maternal fibroblasts (p < 0.05). Maternal fibroblasts proliferated more with IGF-I than IGF-II (p < 0.001). Fetal fibroblasts responded to IGF-II slightly better than IGF-I and significantly greater than maternal cells (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Fetal intestinal fibroblasts respond to IGF-II with greater proliferation and do not have the increased IGFBPs seen post-confluence in adult intestinal fibroblasts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein production: studies in fetal, postnatal, and pregnant sheep.J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jul;152(1):19-27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520104. J Cell Physiol. 1992. PMID: 1377698
-
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs), and proteolyzed IGFBP-3 in embryonic cavities in early human pregnancy: their potential relevance to maternal-embryonic and fetal interactions.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Nov;79(5):1249-55. doi: 10.1210/jcem.79.5.7525630. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. PMID: 7525630
-
Evidence for a novel insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-dependent protease regulating IGF-binding protein-4 in dermal fibroblasts.Endocrinology. 1992 Nov;131(5):2071-6. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.5.1385096. Endocrinology. 1992. PMID: 1385096
-
[Physiological significance of IGF-I and its binding proteins on fetal growth and maturation].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1994 Aug;46(8):660-72. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1994. PMID: 7522266 Review. Japanese.
-
Spatial and temporal patterns of expression of messenger RNA for insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in the placenta of man and laboratory animals.Placenta. 2000 May;21(4):289-305. doi: 10.1053/plac.1999.0498. Placenta. 2000. PMID: 10833363 Review.
Cited by
-
Dermal fibroblasts derived from fetal and postnatal humans exhibit distinct responses to insulin like growth factors.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 Nov 7;7:124. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-124. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17988375 Free PMC article.
-
Chemically induced transformation of human dermal fibroblasts to hair-inducing dermal papilla-like cells.Cell Prolif. 2019 Sep;52(5):e12652. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12652. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 31264301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Olney RC, Wilson DM, Mohtai M, Fielder PJ, Smith RL. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-a increase insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) production and IGFBP-3 protease activity in human articular chondrocytes. J Endocrinol. 1995;146:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Schuller AGP, van Neck JW, Lindenbergh-Kortleve DJ, Groffen C, de Jong I, Zwarthoff EC, Drop SLS. Gene expression of the IGF binding proteins during post-implantation embryogensis of the mouse; comparison with the expression of IGF-I and -II and their receptors in rodent and human. In: LeRoith D and Raizada MK, editor. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. New York, Plenum Press; 1994. pp. 267–277. (Current Directions in Insulin-like Growth Factor Research). - PubMed
-
- Freier S, Eran M, Reinus C, Ariel I, Faber J, Wilschanski M, Braverman D. Relative expression of the insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in the fetal, child and adult stomach and intestine. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;40:202–209. doi: 10.1097/00005176-200502000-00023. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

