Developmental programming of health and disease
- PMID: 16441949
- PMCID: PMC1885472
- DOI: 10.1079/pns2005478
Developmental programming of health and disease
Abstract
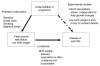
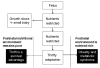
The environment encountered in fetal and neonatal life exerts a profound influence on physiological function and risk of disease in adult life. Epidemiological evidence suggests that impaired fetal growth followed by rapid catch-up in infancy is a strong predictor of obesity, hypertension, non-insulin-dependent diabetes and CHD. Whilst these associations have been widely accepted to be the product of nutritional factors operating in pregnancy, evidence from human populations to support this assertion is scarce. Animal studies clearly demonstrate that there is a direct association between nutrient imbalance in fetal life and later disease states, including hypertension, diabetes, obesity and renal disease. These associations are independent of changes in fetal growth rates. Experimental studies examining the impact of micro- or macronutrient restriction and excess in rodent pregnancy provide clues to the mechanisms that link fetal nutrition to permanent physiological changes that promote disease. Exposure to glucocorticoids in early life appears to be an important consequence of nutrient imbalance and may lead to alterations in gene expression that have major effects on tissue development and function. Epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation, may also be important processes in early-life programming.
Figures
References
-
- Barker DJ. The developmental origins of chronic adult disease. Acta Paediatrica. 2004;93(Suppl):26–33. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Hales CN, Fall CH, Osmond C, Phipps K, Clark PM. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia (syndrome X): relation to reduced fetal growth. Diabetologia. 1993a;36:62–67. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ, Osmond C. Infant mortality, childhood nutrition, and ischaemic heart disease in England and Wales. Lancet. 1986;i:1077–1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

