Behavioral and neurobiological effects of the enkephalinase inhibitor RB101 relative to its antidepressant effects
- PMID: 16442521
- PMCID: PMC1828120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.002
Behavioral and neurobiological effects of the enkephalinase inhibitor RB101 relative to its antidepressant effects
Abstract
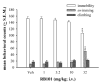
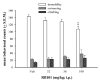
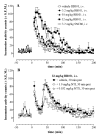
Nonpeptidic delta-opioid receptor agonists produce antidepressant-like effects in rodents, and compounds that inhibit the breakdown of endogenous opioid peptides have antidepressant-like effects in animal models. In this study, the behavioral effects of the enkephalinase inhibitor, RB101 (N-[(R, S)-2-benzyl-3-[(S)(2-amino-4-methyl-thio)-butyldithio]-1-oxopropyl]-l-phenylalanine benzyl ester), were examined. Specifically, the effects of RB101 on convulsive activity, locomotor activity, and antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test were studied in Sprague-Dawley rats, and the opioid receptor types mediating these effects were examined by antagonist studies. In addition, the effects of RB101 on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA expression were evaluated in relation to its antidepressant effects. RB101 produced delta-opioid receptor-mediated antidepressant effects (32 mg/kg i.v. and 100 mg/kg i.p.) and increased locomotor activity (32 mg/kg i.v.) in rats. RB101 did not produce convulsions or seizures and did not alter BDNF mRNA expression. In conclusion, RB101 has the potential to produce antidepressant effects without convulsions.
Figures
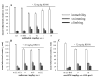


 ), 10 mg/kg naltrindole (s.c.) ((
), 10 mg/kg naltrindole (s.c.) ((
 ), and 10 mg/kg naltrindole given 15 min prior to 32 mg/kg RB101 ((
), and 10 mg/kg naltrindole given 15 min prior to 32 mg/kg RB101 ((
 ) on BDNF mRNA expression, in comparison to vehicle controls ((
) on BDNF mRNA expression, in comparison to vehicle controls ((
 ). Quantification of BDNF mRNA signal was obtained from photomicrographs of X-ray films exposed for 14 days after in situ hybridization with the antisense cRNA probe to rat BDNF mRNA. BDNF mRNA levels were obtained from frontal cortex, and three hippocampal subfields, the CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus regions (panel A), and from the basolateral amygdale (BLA), endopiriform nucleus (EN), and olfactory cortex (Olf. Ctx.) (panel B). Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M.
). Quantification of BDNF mRNA signal was obtained from photomicrographs of X-ray films exposed for 14 days after in situ hybridization with the antisense cRNA probe to rat BDNF mRNA. BDNF mRNA levels were obtained from frontal cortex, and three hippocampal subfields, the CA1, CA3, and dentate gyrus regions (panel A), and from the basolateral amygdale (BLA), endopiriform nucleus (EN), and olfactory cortex (Olf. Ctx.) (panel B). Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M.References
-
- Baamonde A, Daugé V, Ruiz-Gayo M, Fulga IG, Turcaud S, Fournié-Zaluski MC, Roques BP. Antidepressant-type effects of endogenous enkephalins protected by systemic RB 101 are mediated by opioid δ and dopamine D1 receptor stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;216:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Baird TJ, Deng SX, Landry DW, Winger G, Woods JH. Natural and artificial enzymes against cocaine. I Monoclonal antibody 15A10 and the reinforcing effects of cocaine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295:1127–1134. - PubMed
-
- Broom DC, Jutkiewicz EM, Folk JE, Traynor JR, Rice KC, Woods JH. Nonpeptidic delta-opioid receptor agonists reduce immobility in the forced swim assay in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002;26:744–755. - PubMed
-
- Calderon SN, Rothman RB, Porreca F, Flippen-Anderson JL, McNutt RW, Xu H, Smith LE, Bilsky EJ, Davis P, Rice KC. Probes for narcotic receptor mediated phenomena. 19 Synthesis of (+)-4-[(αR)-α-((2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3-methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide (SNC80): a highly selective, nonpeptide delta opioid receptor agonist. J Med Chem. 1994;37:2125–2128. - PubMed
-
- Comer SD, Hoenicke EM, Sable AI, McNutt RW, Chang KJ, De Costa BR, Mosberg HI, Woods JH. Convulsive effects of systemic administration of the delta opioid agonist BW373U86 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;267:888–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

