Immunomodulatory effects of maternal atrazine exposure on male Balb/c mice
- PMID: 16443249
- PMCID: PMC2034295
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.12.006
Immunomodulatory effects of maternal atrazine exposure on male Balb/c mice
Abstract
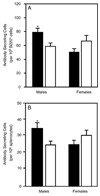
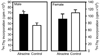
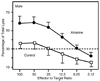
Atrazine is a widely used herbicide applied to corn, sugar and other crops as a broad leaf weed inhibitor. Using the Balb/c mouse model, we have determined that prenatal/lactational exposure to atrazine alters adult immune function. Pregnant Balb/c dams were exposed subcutaneously for 21 days via time release pellets to 700 microg per day of atrazine beginning between days 10 and 12 of pregnancy. Prenatal/Lactational exposure caused no overt physical malformations in the offspring and had no effect on the number of litters carried to term or the litter size. Upon reaching early adulthood (approximately 3 months of age), the state of their immune system was evaluated. There were no changes in body weight or in the organ to body weight ratio of the spleen. Additionally, no changes were observed in the number of CD8+ T cell, CD4+ T cell, or B220+ B cell subpopulations in the spleen. T cell function was assessed by measuring proliferation and cytolytic activity after in vitro allogeneic stimulation. Male mice which had been prenatally/lactationally exposed to atrazine had an increase in both T cell proliferation and cytolytic activity. The humoral immune response was assessed after immunization with heat killed Streptococcus pneumoniae (HKSP). There was a significant increase in the number of HKSP-specific IgM secreting B cells in the spleen of prenatal/lactational exposed male mice. Inasmuch as atrazine is a widespread environmental contaminant, this immunopotentiation raises concerns that it may potentiate clinical diseases, such as autoimmune disease and hypersensitivity, and needs to be carefully monitored and studied.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Developmental immunotoxicity of atrazine in rodents.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 Feb;102(2):139-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00175.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18226067 Review.
-
Long-term Immunotoxic Effects of Oral Prenatal and Neonatal Atrazine Exposure.Toxicol Sci. 2019 Apr 1;168(2):497-507. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfz005. Toxicol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30629250 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotoxic effects of short-term atrazine exposure in young male C57BL/6 mice.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Aug;86(2):324-32. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi188. Epub 2005 May 11. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15888671
-
Developmental atrazine exposure suppresses immune function in male, but not female Sprague-Dawley rats.Toxicol Sci. 2003 Dec;76(2):366-75. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfg250. Epub 2003 Sep 26. Toxicol Sci. 2003. PMID: 14514952
-
Environmental toxicants and the developing immune system: a missing link in the global battle against infectious disease?Reprod Toxicol. 2011 Apr;31(3):327-36. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Reprod Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 20851760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Demasculinization and feminization of male gonads by atrazine: consistent effects across vertebrate classes.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Oct;127(1-2):64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.03.015. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21419222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative effects of low dose atrazine exposure on the development of effective immunity to FV3 in Xenopus laevis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Nov;47(1):52-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24984115 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Atrazine on the Development of Neural System of Zebrafish, Danio rerio.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:976068. doi: 10.1155/2015/976068. Epub 2015 May 31. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26114119 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic atrazine exposure increases the expression of genes associated with GABAergic and glutamatergic systems in the brain of male albino rat.Front Toxicol. 2022 Aug 22;4:933300. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.933300. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36071823 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S254-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv039. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26106142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adgate JL, Barr DB, Clayton CA, Eberly LE, Freeman NC, Lioy PJ, Needham LL, Pellizzari ED, Quackenboss JJ, Roy A, Sexton K. Measurement of children’s exposure to pesticides: analysis of urinary metabolite levels in a probability‐based sample. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001;109(6):583–590. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balduini L, Matoga M, Cavalli E, Seilles E, Riethmuller D, Thomassin M, Guillaume YC. Triazinic herbicide determination by gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry in breast milk. J. Chromatogr., B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003;794:389–395. - PubMed
-
- Blaylock BL, Holladay SD, Comment CE, Heindel JJ, Luster MI. Exposure to tetrachlorodibenzo‐p‐dioxin (TCDD) alters fetal thymocyte maturation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1992;112:207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

