Selection of biocatalysts for chemical synthesis
- PMID: 16446453
- PMCID: PMC1413619
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504733102
Selection of biocatalysts for chemical synthesis
Abstract
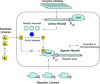
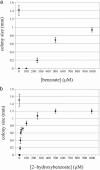
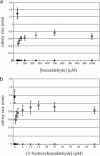
To determine whether microbial chemosensors can be used to find new or better biocatalysts, we constructed Escherichia coli hosts that recognize the product of a biocatalytic conversion through the transcriptional activator NahR and respond by expression of a lacZ or tetA reporter gene. Equipped with a benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (XylC from Pseudomonas putida), the lacZ-based host responded to the oxidation of benzaldehyde and 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde to the corresponding benzoic acids by forming blue colonies, whereas XylC- cells did not. Similarly, the tetA-based host was able to grow under selective conditions only when equipped with XylC, enabling selection of biocatalytically active cells in inactive populations at frequencies as low as 10(-6).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The design of a new mutation model for active genes: expression of the Escherichia coli lac operon in mammalian cells.Mutat Res. 1997 Sep;382(1-2):21-33. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5726(97)00006-x. Mutat Res. 1997. PMID: 9360635
-
Overlapping substrate specificities of benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (the xylC gene product) and 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (the xylG gene product) encoded by TOL plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida.J Bacteriol. 1995 Mar;177(5):1196-201. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.5.1196-1201.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7868591 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive toolbox for the rapid construction of lacZ fusion reporters.J Microbiol Methods. 2012 Dec;91(3):537-43. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.09.023. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Microbiol Methods. 2012. PMID: 23022912
-
Candida glabrata shuttle vectors suitable for translational fusions to lacZ and use of beta-galactosidase as a reporter of gene expression.Gene. 2000 Apr 4;246(1-2):151-5. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00065-2. Gene. 2000. PMID: 10767536
-
Monitoring aromatic hydrocarbons by whole cell electrochemical biosensors.Anal Biochem. 2004 Dec 15;335(2):175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2004.08.032. Anal Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15556555
Cited by
-
Synthetic biosensors for precise gene control and real-time monitoring of metabolites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 3;43(15):7648-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv616. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26152303 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic optimization of styrene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3).Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Jan 25;11:14. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1017-z. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 29416559 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulosic hydrolysate toxicity and tolerance mechanisms in Escherichia coli.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2009 Oct 15;2:26. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-2-26. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2009. PMID: 19832972 Free PMC article.
-
A general strategy for the evolution of bond-forming enzymes using yeast display.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 12;108(28):11399-404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101046108. Epub 2011 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21697512 Free PMC article.
-
Product-induced gene expression, a product-responsive reporter assay used to screen metagenomic libraries for enzyme-encoding genes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Nov;76(21):7029-35. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00464-10. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20833789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faber K., editor. Biotransformations in Organic Chemistry. 3rd Ed. New York: Springer; 1997.
-
- Schmid A., Hollmann F., Park J. B., Bühler B. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002;13:359–366. - PubMed
-
- Straathof A. J. J., Panke S., Schmid A. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002;13:548–556. - PubMed
-
- Schmid A., Dordick J. S., Hauer B., Kiener A., Wubbolts M., Witholt B. Nature. 2001;409:258–268. - PubMed
-
- Goddard J.-P., Reymond J.-L. Trends Biotechnol. 2004;22:363–370. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

