Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1
- PMID: 16446457
- PMCID: PMC1413621
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505667103
Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1
Abstract
bZIP-type transcription factors AREBs/ABFs bind an abscisic acid (ABA)-responsive cis-acting element named ABRE and transactivate downstream gene expression in Arabidopsis. Because AREB1 overexpression could not induce downstream gene expression, activation of AREB1 requires ABA-dependent posttranscriptional modification. We confirmed that ABA activated 42-kDa kinase activity, which, in turn, phosphorylated Ser/Thr residues of R-X-X-S/T sites in the conserved regions of AREB1. Amino acid substitutions of R-X-X-S/T sites to Ala suppressed transactivation activity, and multiple substitution of these sites resulted in almost complete suppression of transactivation activity in transient assays. In contrast, substitution of the Ser/Thr residues to Asp resulted in high transactivation activity without exogenous ABA application. A phosphorylated, transcriptionally active form was achieved by substitution of Ser/Thr in all conserved R-X-X-S/T sites to Asp. Transgenic plants overexpressing the phosphorylated active form of AREB1 expressed many ABA-inducible genes, such as RD29B, without ABA treatment. These results indicate that the ABA-dependent multisite phosphorylation of AREB1 regulates its own activation in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

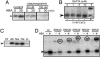

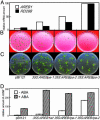
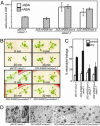
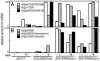
References
-
- Leung J., Giraudat J. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998;49:199–222. - PubMed
-
- Himmelbach A., Yang Y., Grill E. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003;6:470–479. - PubMed
-
- Koornneef M., Jorna M. L., Brinkhorst-van der Swan D. L. C., Karssen C. M. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1982;61:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Leung J., Bouvier-Durand M., Morris P. C., Guerrier D., Chefdor F., Giraudat J. Science. 1994;264:1448–1452. - PubMed
-
- Meyer K., Leube M. P., Grill E. Science. 1994;264:1452–1455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

