Comparison between radiological and nasopharyngolaryngoscopic assessment of adenoid tissue volume in mouth breathing children
- PMID: 16446887
- PMCID: PMC9443499
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)31280-5
Comparison between radiological and nasopharyngolaryngoscopic assessment of adenoid tissue volume in mouth breathing children
Abstract
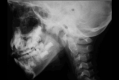
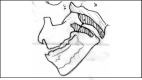
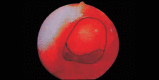
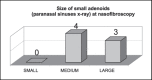
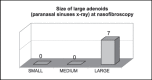
The pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid) constitutes the upper portion of the Waldeyer's ring and is located at the top of the nasopharynx, next to the auditory tube and choana. It plays an important role in recurrent otitis of the middle ear and many times its enlargement is responsible for upper airway obstruction. Tonsillectomy is often the treatment of choice for tonsillar diseases. So far, it is the most frequent and one of the oldest surgical procedures performed in children and young adults. The criteria for tonsillectomy, its effect on patient's immunological integrity and the surgical risks are widely controversial. Image study using paranasal sinuses x-ray is a very simple, easy and comfortable method to evaluate the sizes of adenoids and the grade of upper airway obstruction. Cohen et al. supported that paranasal sinuses x-ray is the best way to determine pharyngeal tonsil hypertrophy. On the other hand, nasopharyngolaryngoscopy can provide more accurate data on the nasopharynx, as it can dynamically reveal its structures and the obstruction status of the upper airway. This study compared the grade of adenoid hypertrophy, as well as upper airway obstruction, using the above-mentioned approaches in children ranging from 3 to 10 years old. The study came to the conclusion that nasopharyngolaryngoscopy is a much more accurate diagnostic procedure than radiological evaluation of the nasopharynx.
Figures


References
-
- Gross CW, Harrison SE. Tonsils and Adenoids Pediatrics. Review. 2000;21(3):75–78. - PubMed
-
- Paulussen C, Claes J, Jorissen M. Adenoids and tonsils indications for surgery and immunological consequences of surgery Acta oto-rhino-laryngologica belg. 2000;54:403–408. - PubMed
-
- Fujioka M, Young LW, Girdany BR. Radiographic-Evaluation of adenoidal size in children: adenoidal-nasopharyngeal ratio AJR. 1979;173:401–404. - PubMed
-
- Chami FAL. Avaliaçã o nasofibroscópica e radiológica de pacientes com Hiperplasia da amígdala faríngea. RBM-ORL. 1998;5(4):118–125.
-
- Cohen ML, Koltai PJ, Scott JR. Lateral cervical radiographs and adenoid size: Do they correlate. ENT Journal. 1992;71(12):638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

