Luffa operculata effects on the epithelium of frog palate: histological features
- PMID: 16446907
- PMCID: PMC9450526
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)31300-8
Luffa operculata effects on the epithelium of frog palate: histological features
Abstract
Luffa operculata is the botanical name of buchinha-do-norte or cabacinha, which is a medicinal plant widely used for the treatment of rhinitis and rhinosinusitis. In Europe and USA, it is available in homeopathic medicines. In Brazil, Luffa operculata dry fruit infusion is inhaled or instilled into the nose releasing profuse mucous secretion, thus relieving nasal symptoms. Nevertheless, this often may cause irritation, epistaxis or anosmia.
Study design: Experimental.
Material and method: The effects of Luffa operculata were evaluated in different concentration infusions, in isolated frog palate preparation, testing 46 palates after immersion. Four groups (n = 10) were tested with the infusion prepared with frog Ringer (isotonic): control; 60 mg/L; 600 mg/L; and 1200 mg/L. An additional group was tested using the infusion with water (600 mg/L H2O, n = 6). Epithelial samples were harvested to be studied under light microscopy and electron transmission microscopy.
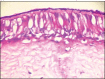
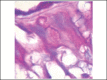
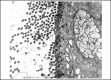
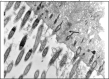
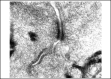
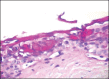
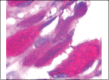
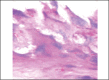
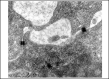
Results: In treated palates, light microscopy findings were dose-dependent standard toxic changes. Electron transmission microscopy showed enlargement of intercellular spaces and tight junctions disruption, pointing to ion-fluid transport abnormalities.
Conclusions: Luffa operculata infusion in currently used doses can promote significant structural and ultrastructural changes in the epithelium of this ex vivo model of respiratory mucosa.
Figures


References
-
- Menon-Miyake MA, Caniello M, Balbani APS, Butugan O. Inquérito sobre o uso de plantas medicinais para tratamento de afecçõ es otorrinolaringológicas entre pacientes de um hospital público terciário. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringologia. 2004;70(2):43–55. Caderno de Debates.
-
- Hughes EF. Overview of complementary, alternative and integrative medicine. Clin Obstet and Gynecol. 2001;44(4):774–779. - PubMed
-
- Marcus DM, Grollman AP. Botanical medicines - The need for new regulations. N Engl J Med. 2002;347(25):2073–2076. - PubMed
-
- Krouse JH, Krouse HJ. Patient use of traditional and complementary therapies in treating rhinosinusitis before consulting an otolaryngologist. Laryngoscope. 1999;109:1223–1227. - PubMed
-
- Dergal JM, Gold JL, Laxer DA, Lee MS, Binns MA, Lanctot KL, Freedman M, Rochon PA. Potential interactions between herbal medicines and conventional drug therapies used by older adults attending a memory clinic. Drug Aging. 2002;19(11):879–886. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

