[Enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome: report of 3 cases and literature review]
- PMID: 16446948
- PMCID: PMC9450622
- DOI: 10.1016/s1808-8694(15)31342-2
[Enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome: report of 3 cases and literature review]
Abstract
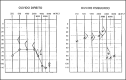
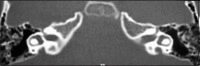
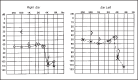
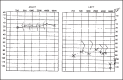
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome is characterized by a widening of the vestibular aqueduct, associated with sensorineural hearing loss, or sometimes with mixed hearing loss, which may be congenital or acquired during childhood. The sensorineural hearing loss may be classified into mild, moderate and severe, associated with sudden periods of improvement or aggravation. The enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct is the most common inner ear anomaly. This syndrome is admitted as a result of a genetic abnormality of the vestibular aqueduct development, previous to the fifth week of gestation. The incidence of this syndrome ranges from 1% to 1.3%, with the possibility of getting up to 7%, depending on the examined population. The aim of this study was to analyze three cases of LVAS seen at the Otorhinolaryngology and Radiology Department of Sao Camilo Hospital - Sao Paulo. Two of these three cases were of brothers, from the same mother but from different fathers. Two were male and one was female and the ages ranged from 9 to 30 years old. The diagnostic method of election was CT - Computerized Tomography of the temporal bones. The recommended management of the cases was conservative, except for those of cranial trauma, barotrauma and, if necessary, the use of hearing aids.
Figures

References
-
- Valvasori GE, Clemis JD. The Large Vestibular Syndrome. Laryngoscope. 1978;88:723–728. - PubMed
-
- Swartz JD, Yussen PS, Mandell DW. The Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome: Computed Tomographic Appearance. Clin Radiol. 1985;36:241–243. - PubMed
-
- Bento RF, Lessa M, Castilho AM, Sanchez TG, Gebrim SEM, Brito Neto RV, Miniti A. Síndrome do Aqueduto Vestibular Alargado: Relato de 3 casos e Revisão de Literatura. Arquivos. 2001;5(1):26–33.
-
- Zazal GH, Tomashi SM, Vezima LG, Bjornst P, Grundfast KM. Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct and Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Childhood. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989;115:54–58. - PubMed
-
- Kodama A, Sando I. Postnatal Development of the Aqueduct Vestibular Endolynfatic Sac. Ann Otol Rhinol Laringol. 1982;91(suppl. 96):3–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

