Progression of regulatory gene expression states in fetal and adult pro-T-cell development
- PMID: 16448545
- PMCID: PMC4157939
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00355.x
Progression of regulatory gene expression states in fetal and adult pro-T-cell development
Abstract
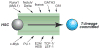
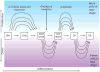
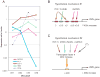
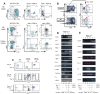
Precursors entering the T-cell developmental pathway traverse a progression of states characterized by distinctive patterns of gene expression. Of particular interest are regulatory genes, which ultimately control the dwell time of cells in each state and establish the mechanisms that propel them forward to subsequent states. Under particular genetic and developmental circumstances, the transitions between these states occur with different timing, and environmental feedbacks may shift the steady-state accumulations of cells in each state. The fetal transit through pro-T-cell stages is faster than in the adult and subject to somewhat different genetic requirements. To explore causes of such variation, this review presents previously unpublished data on differentiation gene activation in pro-T cells of pre-T-cell receptor-deficient mutant mice and a quantitative comparison of the profiles of transcription factor gene expression in pro-T-cell subsets of fetal and adult wildtype mice. Against a background of consistent gene expression, several regulatory genes show marked differences between fetal and adult expression profiles, including those encoding two basic helix-loop-helix antagonist Id factors, the Ets family factor SpiB and the Notch target gene Deltex1. The results also reveal global differences in regulatory alterations triggered by the first T-cell receptor-dependent selection events in fetal and adult thymopoiesis.
Figures

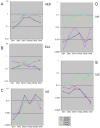
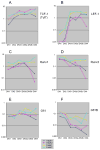
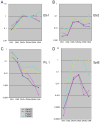
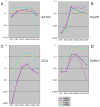
References
-
- Rothenberg EV, Taghon T. Molecular Genetics of T Cell Development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:601–49. - PubMed
-
- Rothenberg EV, Anderson MK. Elements of transcription factor network design for T-lineage specification. Devel Biol. 2002;246:29–44. - PubMed
-
- Han H, Tanigaki K, Yamamoto N, Kuroda K, Yoshimoto M, Nakahata T, Ikuta K, Honjo T. Inducible gene knockout of transcription factor recombination signal binding protein-J reveals its essential role in T versus B lineage decision. Int Immunol. 2002;14:637–45. - PubMed
-
- Tanigaki K, Tsuji M, Yamamoto N, Han H, Tsukada J, Inoue H, Kubo M, Honjo T. Regulation of αβ/γδ T cell lineage commitment and peripheral T cell responses by Notch/RBP-J signaling. Immunity. 2004;20:611–22. - PubMed
-
- Maillard I, Weng AP, Carpenter AC, Rodriguez CG, Sai H, Xu L, Allman D, Aster JC, Pear WS. Mastermind critically regulates Notch-mediated lymphoid cell fate decisions. Blood. 2004;104:1696–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

