Psychosis among "healthy" siblings of schizophrenia patients
- PMID: 16448569
- PMCID: PMC1434733
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-6-6
Psychosis among "healthy" siblings of schizophrenia patients
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia aggregates in families and accurate diagnoses are essential for genetic studies of schizophrenia. In this study, we investigated whether siblings of patients with schizophrenia can be identified as free of any psychotic disorder using only register information. We also analyzed the emergence of psychotic disorders among siblings of patients with schizophrenia during seven to eleven years of follow-up.
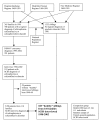
Methods: A genetically homogenous population isolate in north-eastern Finland having 365 families with 446 patients with a diagnosis of schizophrenia was initially identified in 1991 using four nationwide registers. Between 1998 and 2002, 124 patients and 183 siblings in 110 families were contacted and interviewed using SCID-I, SCID-II and SANS. We also compared the frequency of mental disorders between siblings and a random population comparison group sample.
Results: Thirty (16%) siblings received a diagnosis of psychotic disorder in the interview. 14 siblings had had psychotic symptoms already before 1991, while 16 developed psychotic symptoms during the follow-up. Over half of the siblings (n = 99, 54%) had a lifetime diagnosis of any mental disorder in the interview.
Conclusion: Register information cannot be used to exclude psychotic disorders among siblings of patients with schizophrenia. The high rate of emergence of new psychotic disorders among initially healthy siblings should be taken into account in genetic analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Kendler KS, McGuire M, Gruenberg AM, O'Hare A, Spellman M, Walsh D. The Roscommon Family Study I. Methods, diagnosis of probands, and risk of schizophrenia in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:527–540. - PubMed
-
- Kendler KS, McGuire M, Gruenberg AM, Spellman M, O'Hare A, Wals D. The Roscommon Family Study, II: the risk of non-schizophrenic nonaffective psychoses in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:645–652. - PubMed
-
- Chang CJ, Chen WJ, Liu SK, Cheng JJ, Yang WC, Cheng HJ, Lane HY, Lin SK, Yang TW, Hwu HG. Morbidity risk of psychiatric disorders among the first degree relatives of schizophrenia patients in Taiwan. Schizophr Bull. 2002;28:379–392. - PubMed
-
- Austin J. Schizophrenia: An update and review. Genetic Counseling. 2005;14:329–340. - PubMed
-
- Kendler KS. Kaplan and Sadock's comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, editor. Schizophrenia. 7. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins. Philadelphia, PA; 2000. pp. 1147–1153.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical