Comprehensive comparative analysis of kinesins in photosynthetic eukaryotes
- PMID: 16448571
- PMCID: PMC1434745
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-18
Comprehensive comparative analysis of kinesins in photosynthetic eukaryotes
Abstract
Background: Kinesins, a superfamily of molecular motors, use microtubules as tracks and transport diverse cellular cargoes. All kinesins contain a highly conserved approximately 350 amino acid motor domain. Previous analysis of the completed genome sequence of one flowering plant (Arabidopsis) has resulted in identification of 61 kinesins. The recent completion of genome sequencing of several photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic eukaryotes that belong to divergent lineages offers a unique opportunity to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of kinesins in plant and non-plant systems and infer their evolutionary relationships.
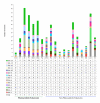
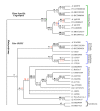
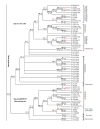
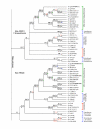
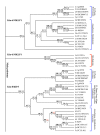
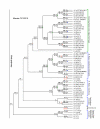
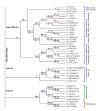
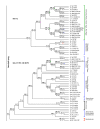
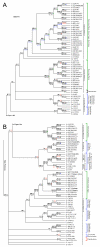
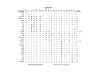
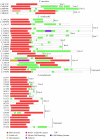
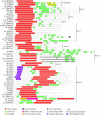
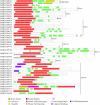
Results: We used the kinesin motor domain to identify kinesins in the completed genome sequences of 19 species, including 13 newly sequenced genomes. Among the newly analyzed genomes, six represent photosynthetic eukaryotes. A total of 529 kinesins was used to perform comprehensive analysis of kinesins and to construct gene trees using the Bayesian and parsimony approaches. The previously recognized 14 families of kinesins are resolved as distinct lineages in our inferred gene tree. At least three of the 14 kinesin families are not represented in flowering plants. Chlamydomonas, a green alga that is part of the lineage that includes land plants, has at least nine of the 14 known kinesin families. Seven of ten families present in flowering plants are represented in Chlamydomonas, indicating that these families were retained in both the flowering-plant and green algae lineages.
Conclusion: The increase in the number of kinesins in flowering plants is due to vast expansion of the Kinesin-14 and Kinesin-7 families. The Kinesin-14 family, which typically contains a C-terminal motor, has many plant kinesins that have the motor domain at the N terminus, in the middle, or the C terminus. Several domains in kinesins are present exclusively either in plant or animal lineages. Addition of novel domains to kinesins in lineage-specific groups contributed to the functional diversification of kinesins. Results from our gene-tree analyses indicate that there was tremendous lineage-specific duplication and diversification of kinesins in eukaryotes. Since the functions of only a few plant kinesins are reported in the literature, this comprehensive comparative analysis will be useful in designing functional studies with photosynthetic eukaryotes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Origin and evolution of Kinesin-like calmodulin-binding protein.Plant Physiol. 2005 Jul;138(3):1711-22. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.060913. Epub 2005 Jun 10. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15951483 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Kinesin Repertoires Expand with New Domain Architecture and Contract with the Loss of Flagella.J Mol Evol. 2024 Aug;92(4):381-401. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10178-9. Epub 2024 Jun 26. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38926179
-
Kinesins in the Arabidopsis genome: a comparative analysis among eukaryotes.BMC Genomics. 2001;2:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-2-2. Epub 2001 Jun 25. BMC Genomics. 2001. PMID: 11472632 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of the Arabidopsis kinesin superfamily of microtubule-based motor proteins.Protoplasma. 2012 Oct;249(4):887-99. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0343-9. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 22038119 Review.
-
Why are ATP-driven microtubule minus-end directed motors critical to plants? An overview of plant multifunctional kinesins.Funct Plant Biol. 2020 May;47(6):524-536. doi: 10.1071/FP19177. Funct Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32336322 Review.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic analysis of the Kinesin superfamily from physcomitrella.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Oct 16;3:230. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00230. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 23087697 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubules contribute to tubule elongation and anchoring of endoplasmic reticulum, resulting in high network complexity in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2014 Dec;166(4):1869-76. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.252320. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25367857 Free PMC article.
-
A kinesin with calponin-homology domain is involved in premitotic nuclear migration.J Exp Bot. 2010 Jul;61(12):3423-37. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq164. Epub 2010 Jun 21. J Exp Bot. 2010. PMID: 20566563 Free PMC article.
-
Kinesin-13 regulates flagellar, interphase, and mitotic microtubule dynamics in Giardia intestinalis.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Dec;6(12):2354-64. doi: 10.1128/EC.00128-07. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17766466 Free PMC article.
-
The kinesin ATK5 functions in early spindle assembly in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2007 Jan;19(1):226-36. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047613. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 17220198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddy ASN. Molecular motors and their functions in plants. Int Rev Cytol & Cell Bio. 2001;204:97–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

