Localized recruitment and activation of RhoA underlies dendritic spine morphology in a glutamate receptor-dependent manner
- PMID: 16449195
- PMCID: PMC2063654
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200506136
Localized recruitment and activation of RhoA underlies dendritic spine morphology in a glutamate receptor-dependent manner
Abstract
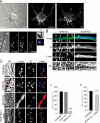
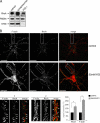
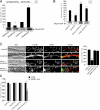
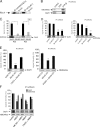
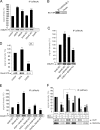
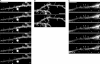
Actin is the major cytoskeletal source of dendritic spines, which are highly specialized protuberances on the neuronal surface where excitatory synaptic transmission occurs (Harris, K.M., and S.B. Kater. 1994. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17:341-371; Yuste, R., and D.W. Tank. 1996. Neuron. 16:701-716). Stimulation of excitatory synapses induces changes in spine shape via localized rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton (Matus, A. 2000. Science. 290:754-758; Nagerl, U.V., N. Eberhorn, S.B. Cambridge, and T. Bonhoeffer. 2004. Neuron. 44:759-767). However, what remains elusive are the precise molecular mechanisms by which different neurotransmitter receptors forward information to the underlying actin cytoskeleton. We show that in cultured hippocampal neurons as well as in whole brain synaptosomal fractions, RhoA associates with glutamate receptors (GluRs) at the spine plasma membrane. Activation of ionotropic GluRs leads to the detachment of RhoA from these receptors and its recruitment to metabotropic GluRs. Concomitantly, this triggers a local reduction of RhoA activity, which, in turn, inactivates downstream kinase RhoA-specific kinase, resulting in restricted actin instability and dendritic spine collapse. These data provide a direct mechanistic link between neurotransmitter receptor activity and the changes in spine shape that are thought to play a crucial role in synaptic strength.
Figures

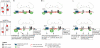
Similar articles
-
Transmitting on actin: synaptic control of dendritic architecture.J Cell Sci. 2007 Jan 15;120(Pt 2):205-12. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03337. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17215449 Review.
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in CA1 region affects synaptic expression of glutamate receptor subunits and associated proteins in the whole hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2006 Sep 1;141(3):1399-413. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.070. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16766131
-
Postsynaptic protein mobility in dendritic spines: long-term regulation by synaptic NMDA receptor activation.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006 Apr;31(4):702-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16504537
-
Activity-induced targeting of profilin and stabilization of dendritic spine morphology.Nat Neurosci. 2003 Nov;6(11):1194-200. doi: 10.1038/nn1135. Epub 2003 Oct 12. Nat Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14555951
-
Synaptic trafficking of glutamate receptors by MAGUK scaffolding proteins.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;17(7):343-52. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.005. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17644382 Review.
Cited by
-
Rho-kinase inhibition has antidepressant-like efficacy and expedites dendritic spine pruning in adolescent mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Apr;124:520-530. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.12.015. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 30593834 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuning of neuronal architecture requires two profilin isoforms.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 7;107(36):15780-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004406107. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20798032 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of the actin cytoskeleton in fear memory formation.Front Behav Neurosci. 2011 Jul 14;5:39. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00039. eCollection 2011. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21808614 Free PMC article.
-
The Correlation Between RhoA Expression and Clinicopathological Characteristics in Gastric Cancer Patients After Curative Surgery.World J Surg. 2015 Sep;39(9):2289-99. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3095-4. World J Surg. 2015. PMID: 26013205
-
INF2-mediated actin filament reorganization confers intrinsic resilience to neuronal ischemic injury.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 13;13(1):6037. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33268-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36229429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baskys, A., and M. Blaabjerg. 2005. Understanding regulation of nerve cell death by mGluRs as a method for development of successful neuroprotective strategies. J. Neurol. Sci. 229-230:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Blaabjerg, M., L. Fang, J. Zimmer, and A. Baskys. 2003. Neuroprotection against NMDA excitotoxicity by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors is associated with reduction of NMDA stimulated currents. Exp. Neurol. 183:573–580. - PubMed
-
- Bonhoeffer, T., and R. Yuste. 2002. Spine motility. Phenomenology, mechanisms, and function. Neuron. 35:1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Bradke, F., and C.G. Dotti. 1997. Videomicroscopy of living microinjected hippocampal neurons in culture. In Microinjection and Transgenesis: Strategies and Protocols. A. Cid-Arregui and A. Garcia-Carrancà, editors. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany. 81–94.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

