Sequence effects of aminofluorene-modified DNA duplexes: thermodynamic and circular dichroism properties
- PMID: 16449208
- PMCID: PMC1356535
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkj480
Sequence effects of aminofluorene-modified DNA duplexes: thermodynamic and circular dichroism properties
Erratum in
- Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(6):1945
Abstract
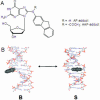
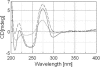
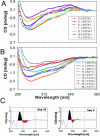
Circular dichroism (CD) and UV-melting experiments were conducted with 16 oligodeoxynucleotides modified by the carcinogen 2-aminofluorene, whose sequence around the lesion was varied systematically [d(CTTCTNG[AF]NCCTC), N = G, A, C, T], to gain insight into the factors that determine the equilibrium between base-displaced stacked (S) and external B-type (B) duplex conformers. Differing stabilities among the duplexes can be attributed to different populations of S and B conformers. The AF modification always resulted in sequence-dependent thermal (T(m)) and thermodynamic (-DeltaG degrees ) destabilization. The population of B-type conformers derived from eight selected duplexes (i.e. -AG*N- and -CG*N-) was inversely proportional to the -DeltaG degrees and T(m) values, which highlights the importance of carcinogen/base stacking in duplex stabilization even in the face of disrupted Watson-Crick base pairing in S-conformation. CD studies showed that the extent of the adduct-induced negative ellipticities in the 290-350 nm range is correlated linearly with -DeltaG degrees and T(m), but inversely with the population of B-type conformations. Taken together, these results revealed a unique interplay between the extent of carcinogenic interaction with neighboring base pairs and the thermodynamic properties of the AF-modified duplexes. The sequence-dependent S/B heterogeneities have important implications in understanding how arylamine-DNA adducts are recognized in nucleotide excision repair.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fluorescence probing of aminofluorene-induced conformational heterogeneity in DNA duplexes.Chem Res Toxicol. 2008 Feb;21(2):445-52. doi: 10.1021/tx7003536. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18193841 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational and thermodynamic properties modulate the nucleotide excision repair of 2-aminofluorene and 2-acetylaminofluorene dG adducts in the NarI sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):3939-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1307. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22241773 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of flanking sequence context on the conformational flexibility of aminofluorene-modified dG adduct in dA mismatch DNA duplexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1628-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1063. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19151371 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structures of aminofluorene [AF]-stacked conformers of the syn [AF]-C8-dG adduct positioned opposite dC or dA at a template-primer junction.Biochemistry. 1999 Aug 17;38(33):10855-70. doi: 10.1021/bi991266p. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10451382
-
Solution conformation of [AF]dG opposite a -2 deletion site in a DNA duplex: intercalation of the covalently attached aminofluorene ring into the helix with base displacement of the C8-modified syn guanine and adjacent unpaired 3'-adenine into the major groove.Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 26;34(51):16641-53. doi: 10.1021/bi00051a012. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 8527437
Cited by
-
DNA base sequence effects on bulky lesion-induced conformational heterogeneity during DNA replication.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 6;46(12):6356-6370. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky409. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29800374 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and thermodynamic insights on acetylaminofluorene-modified deletion DNA duplexes as models for frameshift mutagenesis.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):937-51. doi: 10.1021/tx400116n. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23688347 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence probing of aminofluorene-induced conformational heterogeneity in DNA duplexes.Chem Res Toxicol. 2008 Feb;21(2):445-52. doi: 10.1021/tx7003536. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18193841 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational and thermodynamic properties modulate the nucleotide excision repair of 2-aminofluorene and 2-acetylaminofluorene dG adducts in the NarI sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):3939-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1307. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22241773 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biochemical impact of C8-aryl-guanine adducts within the NarI recognition DNA sequence: influence of aryl ring size on targeted and semi-targeted mutagenicity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Dec 1;42(21):13405-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1093. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25361967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heflich R.H., Neft R.E. Genetic toxicity of 2-acetylaminofluorene, 2-aminofluorene and some of their metabolites and model metabolites. Mutat. Res. 1994;318:73–114. - PubMed
-
- Beland F.A., Kadlubar F.F. Metabolic activation and DNA adducts of aromatic amines and nitroaromatic hydrocarbons. In: Cooper C.S., Grover P.L., editors. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1990. pp. 267–325.
-
- Gillet L.C., Scharer O.D. Molecular mechanisms of mammalian global genome nucleotide excision repair. Chem. Rev. 2006 DOI: 10.1021/cr040483f, http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr040483f - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cui X.S., Eriksson L.C., Moller L. Formation and persistence of DNA adducts during and after a long-term administration of 2-nitrofluorene. Mutat Res. 1999;442:9–18. - PubMed

