Serial measurement of BCR-ABL transcripts in the peripheral blood after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia: an attempt to define patients who may not require further therapy
- PMID: 16449534
- PMCID: PMC1895293
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3320
Serial measurement of BCR-ABL transcripts in the peripheral blood after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia: an attempt to define patients who may not require further therapy
Abstract
We identified 243 patients with Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who had BCR-ABL transcripts monitored by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for a median of 84.3 months. Individual patients were regarded as having achieved molecular relapse (MR) if the BCR-ABL/ABL ratio exceeded 0.02% on 3 occasions or reached 0.05% on 2 occasions. Patients were allocated to 1 of 4 categories: (1) 36 patients were "persistently negative" or had a single low-level positive result; (2) 51 patients, "fluctuating positive, low level," had more than 1 positive result but never more than 2 consecutive positive results; (3) 27 patients, "persistently positive, low level," had persisting low levels of BCR-ABL transcripts but never more than 3 consecutive positive results; and (4) 129 patients relapsed. In 107 of these, relapse was based initially only on molecular criteria; in 72 (67.3%) patients the leukemia progressed to cytogenetic or hematologic relapse either prior to or during treatment with donor lymphocyte infusions. We conclude that the pattern of BCR-ABL transcript levels after allograft is variable; only a minority of patients with fluctuating or persistent low levels of BCR-ABL transcripts satisfied our definitions of MR, whereas the majority of patients who did so were likely to progress further.
Figures

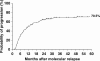
Similar articles
-
Molecular analysis of lineage-specific chimerism and minimal residual disease by RT-PCR of p210(BCR-ABL) and p190(BCR-ABL) after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia: increasing mixed myeloid chimerism and p190(BCR-ABL) detection precede cytogenetic relapse.Blood. 2000 Apr 15;95(8):2659-65. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10753848
-
Molecular monitoring of BCR-ABL transcripts after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013 May;19(5):735-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.01.007. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23333776
-
Early detection of BCR-ABL transcripts by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction predicts outcome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2001 Mar 15;97(6):1560-5. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.6.1560. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11238091
-
Molecular basis for therapeutic decisions in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation.Haematologica. 2000 Oct;85(10):1072-82. Haematologica. 2000. PMID: 11025600 Review.
-
Minimal residual disease in chronic myeloid leukaemia.Hematol Cell Ther. 1998 Oct;40(5):224-8. Hematol Cell Ther. 1998. PMID: 9844816 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep molecular responses for treatment-free remission in chronic myeloid leukemia.Cancer Med. 2016 Sep;5(9):2398-411. doi: 10.1002/cam4.801. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27367039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Relapsing 25 Years after Allogenic Stem Cell Transplantation.Case Rep Hematol. 2018 Sep 23;2018:2045985. doi: 10.1155/2018/2045985. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30345125 Free PMC article.
-
Effective use of imatinib-mesylate in the treatment of relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic transplantation.Haematologica. 2009 Feb;94(2):296-8. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13353. Epub 2008 Dec 23. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19109219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Transplantation in CML in the TKI era: who, when, and how?Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022 Dec 9;2022(1):114-122. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2022000329. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022. PMID: 36485123 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results.Blood. 2006 Jul 1;108(1):28-37. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-0092. Epub 2006 Mar 7. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16522812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clift RA, Buckner CD, Thomas ED, et al. The treatment of chronic granulocytic leukaemia in chronic phase by allogeneic marrow transplantation. Lancet. 1982;2: 261-263. - PubMed
-
- Goldman JM, Baughan ASJ, McCarthy DM, et al. Marrow transplantation for patients in the chronic phase of chronic granulocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1982;2: 623-625. - PubMed
-
- Thomas ED, Clift RA, Fefer A, et al. Marrow transplantation for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104: 155-163. - PubMed
-
- Goldman JM, Apperley JF, Jones LM, et al. Bone marrow transplantation for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1986;314: 202-207. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz MM, Rowlings PA, Passweg JR, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for CML: a report from the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996;17(suppl 3): S5-S6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

