AP-1 differentially expressed proteins Krp1 and fibronectin cooperatively enhance Rho-ROCK-independent mesenchymal invasion by altering the function, localization, and activity of nondifferentially expressed proteins
- PMID: 16449658
- PMCID: PMC1367185
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.4.1480-1495.2006
AP-1 differentially expressed proteins Krp1 and fibronectin cooperatively enhance Rho-ROCK-independent mesenchymal invasion by altering the function, localization, and activity of nondifferentially expressed proteins
Abstract
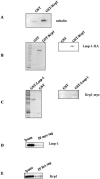
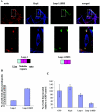
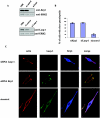
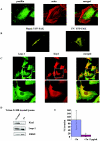
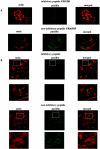
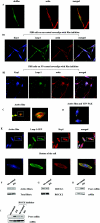
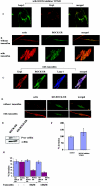
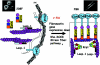
The transcription factor AP-1, which is composed of Fos and Jun family proteins, plays an essential role in tumor cell invasion by altering gene expression. We report here that Krp1, the AP-1 up-regulated protein that has a role in pseudopodial elongation in v-Fos-transformed rat fibroblast cells, forms a novel interaction with the nondifferentially expressed actin binding protein Lasp-1. Krp1 and Lasp-1 colocalize with actin at the tips of pseudopodia, and this localization is maintained by continued AP-1 mediated down-regulation of fibronectin that in turn suppresses integrin and Rho-ROCK signaling and allows pseudopodial protrusion and mesenchyme-like invasion. Mutation analysis of Lasp-1 demonstrates that its SH3 domain is necessary for pseudopodial extension and invasion. The results support the concept of an AP-1-regulated multigenic invasion program in which proteins encoded by differentially expressed genes direct the function, localization, and activity of proteins that are not differentially expressed to enhance the invasiveness of cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel beta-propeller of the BTB-Kelch protein Krp1 provides a binding site for Lasp-1 that is necessary for pseudopodial extension.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 30;284(44):30498-507. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023259. Epub 2009 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19726686 Free PMC article.
-
Krp1, a novel kelch related protein that is involved in pseudopod elongation in transformed cells.Oncogene. 2000 Mar 2;19(10):1266-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203433. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10713668
-
Regulation of a multigenic invasion programme by the transcription factor, AP-1: re-expression of a down-regulated gene, TSC-36, inhibits invasion.Oncogene. 2000 Nov 9;19(47):5348-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203927. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11103936
-
Rho/ROCK-dependent pseudopodial protrusion and cellular blebbing are regulated by p38 MAPK in tumour cells exhibiting autocrine c-Met activation.Biol Cell. 2006 Jun;98(6):337-51. doi: 10.1042/BC20050088. Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16448388
-
Invasion is a genetic program regulated by transcription factors.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006 Feb;16(1):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2005.12.012. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2006. PMID: 16377173 Review.
Cited by
-
An update on the LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (LASP1): a versatile structural, signaling, and biomarker protein.Oncotarget. 2015 Jan 1;6(1):26-42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3083. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25622104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rho GTPase effector ROCK regulates cyclin A, cyclin D1, and p27Kip1 levels by distinct mechanisms.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;26(12):4612-27. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02061-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16738326 Free PMC article.
-
The LIM and SH3 domain protein family: structural proteins or signal transducers or both?Mol Cancer. 2008 Apr 17;7:31. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-31. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18419822 Free PMC article.
-
LASP1, CERS6, and Actin Form a Ternary Complex That Promotes Cancer Cell Migration.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 16;15(10):2781. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102781. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345118 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization and cytosolic overexpression of LASP-1 correlates with tumor size and nodal-positivity of human breast carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2007 Oct 23;7:198. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-198. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17956604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J., R. Kelso, and L. Cooley. 2000. The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 10:17-24. - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu, H., K. Ichihara-Tanaka, K. Ozono, W. Kamiike, H. Matsuda, and K. Sekiguchi. 1996. Suppression of transformed phenotypes of human fibrosarcoma cells by overexpression of recombinant fibronectin. Cancer Res. 56:4541-4546. - PubMed
-
- Ali, I. U., V. Mautner, R. Lanza, and R. O. Hynes. 1977. Restoration of normal morphology, adhesion and cytoskeleton in transformed cells by addition of a transformation-sensitive surface protein. Cell 11:115-126. - PubMed
-
- Bahassi, E. M., S. Karyala, C. R. Tomlinson, M. A. Sartor, M. Medvedovic, and R. F. Hennigan. 2004. Critical regulation of genes for tumor cell migration by AP-1. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 21:293-304. - PubMed
-
- Bakin, A. V., and T. Curran. 1999. Role of DNA 5-methylcytosine transferase in cell transformation by fos. Science 283:387-390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
