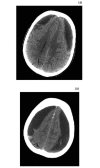
Bilateral chronic subdural haematoma: a reversible cause of parkinsonism
- PMID: 16449784
- PMCID: PMC1360497
- DOI: 10.1177/014107680609900223
Bilateral chronic subdural haematoma: a reversible cause of parkinsonism
Figures
Comment in
-
Bilateral chronic subdural haematoma.J R Soc Med. 2006 Aug;99(8):386. doi: 10.1177/014107680609900810. J R Soc Med. 2006. PMID: 16893934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Krul JM, Wokke JH. Bilateral subdural hematoma presenting as subacute parkinsonism. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 1987;89: 107-9 - PubMed
-
- Sandyk R. Parkinsonism caused by chronic subdural haematoma. A case report. S Afr Med J 1982;61: 595-6 - PubMed
-
- Hageman AT, Horstink MW. Parkinsonism due to a subdural hematoma. Mov Disord 1994;9: 107-8 - PubMed
-
- Chou SM, Gutmann L. Deteriorating parkinsonism and subdural hematomas. Neurology 2001;57: 1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources