Inhibitory effects of retinoic acid metabolism blocking agents (RAMBAs) on the growth of human prostate cancer cells and LNCaP prostate tumour xenografts in SCID mice
- PMID: 16449997
- PMCID: PMC2361176
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602971
Inhibitory effects of retinoic acid metabolism blocking agents (RAMBAs) on the growth of human prostate cancer cells and LNCaP prostate tumour xenografts in SCID mice
Abstract
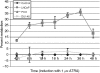
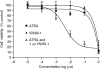
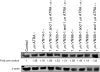
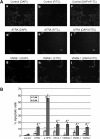
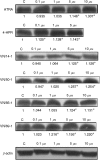
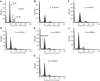
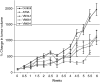
In recent studies, we have identified several highly potent all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) metabolism blocking agents (RAMBAs). On the basis of previous effects of liarozole (a first-generation RAMBA) on the catabolism of ATRA and on growth of rat Dunning R3227G prostate tumours, we assessed the effects of our novel RAMBAs on human prostate tumour (PCA) cell lines. We examined three different PCA cell lines to determine their capacity to induce P450-mediated oxidation of ATRA. Among the three different cell lines, enhanced catabolism was detected in LNCaP, whereas it was not found in PC-3 and DU-145. This catabolism was strongly inhibited by our RAMBAs, the most potent being VN/14-1, VN/50-1, VN/66-1, and VN/69-1 with IC50 values of 6.5, 90.0, 62.5, and 90.0 nM, respectively. The RAMBAs inhibited the growth of LNCaP cells with IC50 values in the microM-range. In LNCaP cell proliferation assays, VN/14-1, VN/50-1, VN/66-1, and VN/69-1 also enhanced by 47-, 60-, 70-, and 65-fold, respectively, the ATRA-mediated antiproliferative activity. We then examined the molecular mechanism underlying the growth inhibitory properties of ATRA alone and in combination with RAMBAs. The mechanism appeared to involve the induction of differentiation, cell-cycle arrest, and induction of apoptosis (TUNEL), involving increase in Bad expression and decrease in Bcl-2 expression. Treatment of LNCaP tumours growing in SCID mice with VN/66-1 and VN/69-1 resulted in modest but statistically significant tumour growth inhibition of 44 and 47%, respectively, while treatment with VN/14-1 was unexpectedly ineffective. These results suggest that some of our novel RAMBAs may be useful agents for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Figures
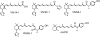

References
-
- Belosay A, Njar VCO, Brodie AMH (2005) Effects and molecular mechanisms of novel retinoic acid metabolism blocking agent (VN/14-1) in MCF-7Ca cells insensitive to aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Clin Cancer Res (in review) - PubMed
-
- Bollag W, Isnardi L, Jablonski S, Klaus M, Majewski S, Pirson W, Toma S (1997) Links between pharmacological properties of retinoids and nuclear retinoid receptors. Int J Cancer 70: 470–472 - PubMed
-
- Campbell MJ, Park S, Uskokovic MR, Dowson MI, Koeffler HP (1998) Expression of retinoic acid receptor-beta sensitizes prostate cancer cells to growth inhibition mediated by combinations with retinoids and a 19-nor hexafluoride vitamin D3 analog. Endocrinology 139: 1927–1980 - PubMed
-
- Carter BS, Carter B, Issacs JT (1990) Epidemiological evidence regarding predisposing factors to prostate cancer. Prostate 16: 187–197 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

