Comparison of marker types and map assumptions using Markov chain Monte Carlo-based linkage analysis of COGA data
- PMID: 16451566
- PMCID: PMC1866829
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S11
Comparison of marker types and map assumptions using Markov chain Monte Carlo-based linkage analysis of COGA data
Abstract
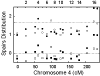
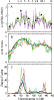
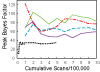
We performed multipoint linkage analysis of the electrophysiological trait ECB21 on chromosome 4 in the full pedigrees provided by the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). Three Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)-based approaches were applied to the provided and re-estimated genetic maps and to five different marker panels consisting of microsatellite (STRP) and/or SNP markers at various densities. We found evidence of linkage near the GABRB1 STRP using all methods, maps, and marker panels. Difficulties encountered with SNP panels included convergence problems and demanding computations.
Figures
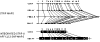
References
-
- Porjesz B, Almasy L, Edenberg HJ, Wang K, Chorlian DB, Foroud T, Goate A, Rice JP, O'Connor SJ, Rohrbaugh J, Kuperman S, Bauer LO, Crowe RR, Schuckit MA, Hesselbrock V, Conneally PM, Tischfield JA, Li TK, Reich T, Begleiter H. Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052716399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pedigree Analysis for Genetics http://www.stat.washington.edu/thompson/Genepi/pangaea.shtml
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

