Linkage analysis of alcohol dependence using MOD scores
- PMID: 16451624
- PMCID: PMC1866771
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S162
Linkage analysis of alcohol dependence using MOD scores
Abstract
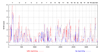
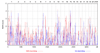
Alcohol dependence is a typical example of a complex trait that is governed by several genes and for which the mode of inheritance is unknown. We analyzed the microsatellite markers and the Affymetrix single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for a subset of the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism family sample, 93 pedigrees of Caucasian ancestry comprising 919 persons, 390 of whom are affected according to DSM III-R and Feighner criteria. In particular, we performed parametric single-marker linkage analysis using MLINK of the LINKAGE package (for the microsatellite data), as well as multipoint MOD-score analysis with GENEHUNTER-MODSCORE (for the microsatellite and SNP data). By use of two liability classes, different penetrances were assigned to males and females. In order to investigate parent-of-origin effects, we calculated MOD scores under trait models with and without imprinting. In addition, for the microsatellite data, the MOD-score analysis was performed with sex-averaged as well as sex-specific maps. The highest linkage peaks were obtained on chromosomes 1, 2, 7, 10, 12, 13, 15, and 21. There was evidence for paternal imprinting at the loci on chromosomes 2, 10, 12, 13, 15, and 21. A tendency to maternal imprinting was observed at two loci on chromosome 7. Our findings underscore the fact that an adequate modeling of the genotype-phenotype relation is crucial for the genetic mapping of a complex trait.
Figures
References
-
- Edenberg HJ, Bierut LJ, Boyce P, Cao M, Cawley S, Chiles R, Doheny KF, Hansen M, Hinrichs A, Jones K, et al. Description of the data from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) and single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for Genetic Analysis Workshop 14. BMC Genetics. 2005;6:S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Third. Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association Press; 1987. pp. 169–170.
-
- Feighner JP, Robins E, Guze SB, Woodruff RA, Jr, Winokur G, Munoz R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972;26:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Lange K, Cantor R, Horvath S, Perola M, Sabatti C, Sinsheimer J, Sobel E. Mendel version 4.0: A complete package for the exact genetic analysis of discrete traits in pedigree and population data sets [abstract] Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69:A1886.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

