Comparison of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellites in detecting quantitative trait loci for alcoholism: the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism
- PMID: 16451661
- PMCID: PMC1866734
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S5
Comparison of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellites in detecting quantitative trait loci for alcoholism: the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism
Abstract
Background: The feasibility of effectively analyzing high-density single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) maps in whole genome scans of complex traits is not known. The purpose of this study was to compare variance components linkage results using different density marker maps in data from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). Marker maps having an average spacing of 10 cM (microsatellite), 0.78 cM (SNP1), and 0.31 cM (SNP2) were used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) affecting maximum number of alcoholic drinks consumed in a 24-hour period (Inmaxalc).
Results: Heritability of Inmaxalc was estimated to be 15%. Multipoint variance components linkage analysis revealed similar linkage patterns among the three marker panels, with the SNP maps consistently yielding higher LOD scores. Robust LOD scores > 1.0 were observed on chromosomes 1 and 13 for all three marker maps. Additional LODs > 1.0 were observed on chromosome 4 with both SNP maps and on chromosomes 18 and 21 with the SNP2 map. Peak LOD scores for Inmaxalc were observed on chromosome 1, although none reached genome-wide statistical significance. Quantile-quantile plots revealed that the multipoint distribution of SNP results appeared to fit the asymptotic null distribution better than the twopoint results.
Conclusion: In conclusion, variance-components linkage analysis using high-density SNP maps provided higher LOD scores compared with the standard microsatellite map, similar to studies using nonparametric linkage methods. Widespread application of SNP maps will depend on further improvements in the computational methods implemented in current software packages.
Figures
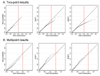
 ; 1/2 point mass 0) for each marker map. The red vertical line corresponds to a LOD score of 1.5.
; 1/2 point mass 0) for each marker map. The red vertical line corresponds to a LOD score of 1.5.Similar articles
-
Genome scan linkage analysis comparing microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms markers for two measures of alcoholism in chromosomes 1, 4, and 7.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S4. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451650 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of age at onset of alcohol dependence: a comparison between microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S12. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451577 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage analysis of complex diseases using microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms: application to alcoholism.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S10. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451555 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of genotyping error in sib-pair genomewide linkage scans depends crucially upon the method of analysis.J Hum Genet. 2005;50(7):329-337. doi: 10.1007/s10038-005-0269-1. Epub 2005 Jul 30. J Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 16059746 Review.
-
Quantitative trait loci for IQ and other complex traits: single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using pooled DNA and microarrays.Genes Brain Behav. 2006;5 Suppl 1:32-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2006.00192.x. Genes Brain Behav. 2006. PMID: 16417615 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-GWAS in Psychiatric Genetics: A Developmental Perspective on the "Other" Next Steps.Genes Brain Behav. 2018 Mar;17(3):e12447. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12447. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Genes Brain Behav. 2018. PMID: 29227573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reich T, Edenberg HJ, Goate A, Williams JT, Rice JP, Van Eerdewegh P, Foroud T, Hesselbrock V, Schuckit MA, Bucholz K, Porjesz B, Li TK, Conneally PM, Nurnberger JI, Jr, Tischfield JA, Crowe RR, Cloninger CR, Wu W, Shears S, Carr K, Crose C, Willig C, Begleiter H. Genome-wide search for genes affecting the risk for alcohol dependence. Am J Med Genet. 1998;81:207–215. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980508)81:3<207::AID-AJMG1>3.0.CO;2-T. - DOI - PubMed
-
- John S, Shephard N, Liu G, Zeggini E, Cao M, Chen W, Vasavda N, Mills T, Barton A, Hinks A, Eyre S, Jones KW, Ollier W, Silman A, Gibson N, Worthington J, Kennedy GC. Whole-genome scan, in a complex disease, using 11,245 single-nucleotide polymorphisms: comparison with microsatellites. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:54–64. doi: 10.1086/422195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Middleton FA, Pato MT, Gentile KL, Morley CP, Zhao X, Eisener AF, Brown A, Petryshen TL, Kirby AN, Medeiros H, Carvalho C, Macedo A, Dourado A, Coelho I, Valente J, Soares MJ, Ferreira CP, Lei M, Azevedo MH, Kennedy JL, Daly MJ, Sklar P, Pato CN. Genomewide linkage analysis of bipolar disorder by use of a high-density single-nucleotide-polymorphism (SNP) genotyping assay: a comparison with microsatellite marker assays and finding of significant linkage to chromosome 6q22. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;74:886–897. doi: 10.1086/420775. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schaid DJ, Guenther JC, Christensen GB, Hebbring S, Rosenow C, Hilker CA, McDonnell SK, Cunningham JM, Slager SL, Blute ML, Thibodeau SN. Comparison of microsatellites versus single-nucleotide polymorphisms in a genome linkage screen for prostate cancer-susceptibility loci. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:948–965. doi: 10.1086/425870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

