Haplotype sharing correlation of alcohol dependence on chromosomes 1-6 in 93 nuclear families
- PMID: 16451693
- PMCID: PMC1866702
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S79
Haplotype sharing correlation of alcohol dependence on chromosomes 1-6 in 93 nuclear families
Abstract
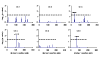
Haplotype data contain signatures of ancestral alleles and increased information for mapping genes associated with complex traits. The motivation of this paper is to test the feasibility of a recently developed haplotype reconstruction algorithm and to perform haplotype-sharing correlation (HSC) analysis in nuclear families using data provided by the Genetic Analysis Workshop 14 and the Collaborative Study of the Genetics of Alcoholism. As an exemplary analysis, haplotype data on chromosomes 1-6 were reconstructed from genotype data in 93 nuclear families by minimizing both the recombinants in within-family haplotypes and the tree distance in between-family haplotypes. HSC analysis was performed using the best set of reconstructed haplotypes, and chromosome-wide significance was evaluated using a permutation procedure. Three markers were found to have significant haplotype associations with DSM-IV alcohol dependence that exceeded the 0.05 level of chromosome-wide significance: marker rs895941 at 36.7 cM on chromosome 3 (p = 0.03), marker rs1631833 at 109.1 cM on chromosome 4 (p = 0.008), and marker rs953887 at 74.2 cM on chromosome 6 (p = 0.02). These results indicated the usefulness of HSC analysis and provided further evidence on chromosome regions associated with alcohol dependence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Haplotype-sharing analysis for alcohol dependence based on quantitative traits and the Mantel statistic.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S75. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451689 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype sharing correlation analysis using family data: a comparison with family-based association test in the presence of allelic heterogeneity.Genet Epidemiol. 2004 Jul;27(1):43-52. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20005. Genet Epidemiol. 2004. PMID: 15185402
-
Linkage and association analyses of microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms in nuclear families.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S25. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451634 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide scanning and fine mapping study of COGA data.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S30. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451640 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide linkage analysis of alcoholism on microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphism data, using alcohol dependence phenotypes and electroencephalogram measures.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S17. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451625 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
More powerful haplotype sharing by accounting for the mode of inheritance.Genet Epidemiol. 2009 Apr;33(3):228-36. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20373. Genet Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 18839399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann L, Fischer C, Deck KG, Nolte IM, te Meerman G, Chang-Claude J. Exploring haplotype sharing methods in general and isolated populations to detect gene(s) of a complex genetic trait. Genet Epidemiol. 2001;21:S554–S559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

