Microsatellite linkage analysis, single-nucleotide polymorphisms, and haplotype associations with ECB21 in the COGA data
- PMID: 16451710
- PMCID: PMC1866685
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S94
Microsatellite linkage analysis, single-nucleotide polymorphisms, and haplotype associations with ECB21 in the COGA data
Abstract
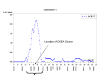
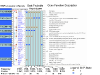
This study, part of the Genetic Analysis Workshop 14 (GAW14), explored real Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism data for linkage and association mapping between genetic polymorphisms (microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)) and beta (16.5-20 Hz) oscillations of the brain rhythms (ecb21). The ecb21 phenotype underwent the statistical adjustments for the age of participants, and for attaining a normal distribution. A total of 1,000 subjects' available phenotypes were included in linkage analysis with microsatellite markers. Linkage analysis was performed only for chromosome 4 where a quantitative trait locus with 5.01 LOD score had been previously reported. Previous findings related this location with the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor. At the same location, our analysis showed a LOD score of 2.2. This decrease in the LOD score is the result of a drastic reduction (one-third) of the available GAW14 phenotypic data. We performed SNP and haplotype association analyses with the same phenotypic data under the linkage peak region on chromosome 4. Seven Affymetrix and two Illumina SNPs showed significant associations with ecb21 phenotype. A haplotype, a combination of SNPs TSC0044171 and TSC0551006 (the latter almost under the region of GABAA genes), showed a significant association with ecb21 (p = 0.015) and a relatively high frequency in the sample studied. Our results affirmed that the GABA region has potential of harboring genes that contribute quantitatively to the beta oscillation of the brain rhythms. The inclusion of the remaining 614 subjects, which in the GAW14 had missing data for the ecb21, can improve the strength of the associations as they have already shown that they contribute quite important information in the linkage analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A genome-wide linkage analysis of alcoholism on microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphism data, using alcohol dependence phenotypes and electroencephalogram measures.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S17. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451625 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of single-nucleotide polymorphisms and microsatellite markers for linkage analysis in the COGA and simulated data sets for Genetic Analysis Workshop 14: Presentation Groups 1, 2, and 3.Genet Epidemiol. 2005;29 Suppl 1:S7-28. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20106. Genet Epidemiol. 2005. PMID: 16342186
-
Genome scan linkage analysis comparing microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphisms markers for two measures of alcoholism in chromosomes 1, 4, and 7.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S4. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451650 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing single-nucleotide polymorphism marker-based and microsatellite marker-based linkage analyses.BMC Genet. 2005 Dec 30;6 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-S1-S13. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 16451588 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and implications of linkage disequilibrium in genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphism and microsatellite panels.Genet Epidemiol. 2005;29 Suppl 1:S72-6. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20112. Genet Epidemiol. 2005. PMID: 16342185
Cited by
-
Genetic influence alters the brain synchronism in perception and timing.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Aug 7;25(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0463-z. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 30086746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haenschel C, Baldeweg T, Croft RJ, Whittington M, Gruzelier J. Gamma and beta frequency oscillations in response to novel auditory stimuli: a comparison of human electroencephalogram (EEG) data with in vitro models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:7645–7650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.120162397. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Porjesz B, Almasy L, Edenberg HJ, Wang K, Chorlian DB, Foroud T, Goate A, Rice JP, O'Connor SJ, Rohrbaugh J, Kuperman S, Bauer LO, Crowe RR, Schuckit MA, Hesselbrock V, Conneally PM, Tischfield JA, Li TK, Reich T, Begleiter H. Linkage disequilibrium between the beta frequency of the human EEG and a GABAA receptor gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;9:3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052716399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

