Epstein-barr virus induced cellular changes in nasal mucosa
- PMID: 16451721
- PMCID: PMC1388193
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-6
Epstein-barr virus induced cellular changes in nasal mucosa
Abstract
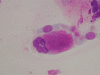
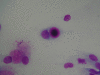
A 21-year-old man presented with nasal obstruction of the right nasal fossa of 1 year duration. Nasal endoscopy revealed in the right inferior turbinate head a rounded neoplasm about 1 cm in diameter. Cytologic study of a nasal scraping specimen disclosed numerous clusters containing columnar cells with cytomegaly, prominent multinucleation, markedly sparse shortened cilia; the cytoplasm contained an acidophil area and a small round area that stained poorly; cells with a large intracytoplasmic vacuole that was acidophil and PAS+. Serology tests using the nested polymer chain reaction (PCR) technique on serum, nasal and pharyngeal smears revealed an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection that was confirmed at electron microscopy. The clinical and cytological features resolved 19 months after the initial evaluation.
Conclusion: The authors advise carrying out clinical (endoscopy, serology, etc.) evaluation of all endonasal neoplasms and to routinely perform cytological study on nasal scraping specimens. When samples test positive for EBV, nasal and nasopharyngeal endoscopy should be performed regularly to detect possible evidence for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Absence of Epstein-Barr virus in olfactory neuroblastoma.Pathology. 2007 Dec;39(6):565-6. doi: 10.1080/00313020701684383. Pathology. 2007. PMID: 18027259
-
Nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and its association with type "i"/XhoI loss strain Epstein-Barr virus in Chile.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Jun;60(6):656-60. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.034199. Epub 2006 Jun 14. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 16775124 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with nasal lymphoma in patients attending the regional hospital of Valdivia, Chile, between 1987 and 2005.J Med Virol. 2010 May;82(5):825-8. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21705. J Med Virol. 2010. PMID: 20336747
-
Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the esophagus.Hum Pathol. 2003 Apr;34(4):407-11. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2003.71. Hum Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12733124 Review.
-
[Clinical, phenotypic and genotypic aspects of nasal T-cell lymphoma and its causal association with Epstein-Barr virus].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Feb;55(2):394-9. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9046830 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Nasal Cytology as a Marker of Atopy in Children.Dis Markers. 2017;2017:4159251. doi: 10.1155/2017/4159251. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Dis Markers. 2017. PMID: 29038613 Free PMC article.
-
Nasal cytology in children: recent advances.Ital J Pediatr. 2012 Sep 25;38:51. doi: 10.1186/1824-7288-38-51. Ital J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23009215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells, a Hallmark of Oncoviruses and a New Therapeutic Challenge.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 14;10:567116. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.567116. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33154944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Nasal Cytology in Respiratory Diseases: Clinical Research and Future Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2025 Jan 29;14(3):884. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030884. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Profile of the Nasal Mucosa in Patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00881-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00881-19. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32094254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meltzer EO, Jalowayski AA. Nasal cytology in clinical practice. Am J Rhinol. 1988;2:47–54.
-
- Gelardi M, Cassano P, Cassano M, Fiorella ML. Nasal cytology: description of a hyperchromatic Supranuclear Stria as a possibile marker for the anatomical and functional integrity of the ciliated cell. Am J Rhinol. 2003;17:263–8. - PubMed
-
- Gelardi M. Atlas of Nasal Cytology. Torino: Centro Scientifico Editore; 2004.
-
- Cassano P, Gelardi M, Fiorella ML, Cassano M. New insights in the treatment of nasal allergy. Arq Otorinol. 2004;8:32–41.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

