NADPH- diaphorase positive cardiac neurons in the atria of mice. A morphoquantitative study
- PMID: 16451738
- PMCID: PMC1373636
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-10
NADPH- diaphorase positive cardiac neurons in the atria of mice. A morphoquantitative study
Abstract
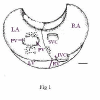
Background: The present study was conducted to determine the location, the morphology and distribution of NADPH-diaphorase positive neurons in the cardiac nerve plexus of the atria of mice (ASn). This plexus lies over the muscular layer of the atria, dorsal to the muscle itself, in the connective tissue of the subepicardium. NADPH- diaphorase staining was performed on whole-mount preparations of the atria mice. For descriptive purposes, all data are presented as means +/- SEM.
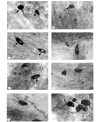
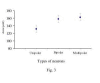
Results: The majority of the NADPH-diaphorase positive neurons were observed in the ganglia of the plexus. A few single neurons were also observed. The number of NADPH-d positive neurons was 57 +/- 4 (ranging from 39 to 79 neurons). The ganglion neurons were located in 3 distinct groups: (1) in the region situated cranial to the pulmonary veins, (2) caudally to the pulmonary veins, and (3) in the atrial groove. The largest group of neurons was located cranially to the pulmonary veins (66.7%). Three morphological types of NADPH-diaphorase neurons could be distinguished on the basis of their shape: unipolar cells, bipolar cells and cells with three processes (multipolar cells). The unipolar neurons predominated (78.9%), whereas the multipolar were encountered less frequently (5,3%). The sizes (area of maximal cell profile) of the neurons ranged from about 90 microm2 to about 220 microm2. Morphometrically, the three types of neurons were similar and there were no significant differences in their sizes. The total number of cardiac neurons (obtained by staining the neurons with NADH-diaphorase method) was 530 +/- 23. Therefore, the NADPH-diaphorase positive neurons of the heart represent 10% of the number of cardiac neurons stained by NADH.
Conclusion: The obtained data have shown that the NADPH-d positive neurons in the cardiac plexus of the atria of mice are morphologically different, and therefore, it is possible that the function of the neurons may also be different.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NADPH diaphorase-positive neurons in the intracardiac plexus of human, monkey and canine right atria.Brain Res. 1996 Jun 17;724(2):256-9. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(96)00314-9. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8828577
-
Distribution of intracardiac neurones and nerve terminals that contain a marker for nitric oxide, NADPH-diaphorase, in the guinea-pig heart.Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Aug;273(2):293-300. doi: 10.1007/BF00312831. Cell Tissue Res. 1993. PMID: 8364971
-
Distribution of NADPH-diaphorase-positive nerves in the uterine cervix and neurons in dorsal root and paracervical ganglia of the female rat.Neurosci Lett. 1992 Dec 7;147(2):224-8. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90601-3. Neurosci Lett. 1992. PMID: 1283461
-
Presence of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in autonomic and sensory ganglion neurons innervating the lacrimal glands of the cat: an immunofluorescent and retrograde tracer double-labeling study.J Chem Neuroanat. 2001 Sep;22(3):147-55. doi: 10.1016/s0891-0618(01)00125-9. J Chem Neuroanat. 2001. PMID: 11522437
-
NADPH-diaphorase-containing cerebrovascular nerve fibres and their possible origin in the pig.J Hirnforsch. 1995;36(3):353-63. J Hirnforsch. 1995. PMID: 7560908
Cited by
-
Distribution of NADPH-diaphorase and AChE activity in the anterior leaflet of rat mitral valve.Eur J Histochem. 2010 Feb 4;54(1):e5. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e5. Eur J Histochem. 2010. PMID: 20353912 Free PMC article.
-
Morphologic pattern of the intrinsic ganglionated nerve plexus in mouse heart.Heart Rhythm. 2011 Mar;8(3):448-54. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.11.019. Epub 2010 Nov 12. Heart Rhythm. 2011. PMID: 21075216 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglionated Plexi Ablation for the Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 24;9(10):3081. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103081. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32987820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anatomical evidence of non-parasympathetic cardiac nitrergic nerve fibres in rat.J Anat. 2021 Jan;238(1):20-35. doi: 10.1111/joa.13291. Epub 2020 Aug 13. J Anat. 2021. PMID: 32790077 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglion cardiacum or juxtaductal body of human fetuses.Anat Cell Biol. 2018 Dec;51(4):266-273. doi: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.4.266. Epub 2018 Dec 29. Anat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30637161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodrigo J, Springall DR, Uttenthal LO, Bentura ML, Abadia-Molina F, Riveros- Moreno V, Martinez-Murillo R, Polak JM, Moncada S. Localization of nitric synthase in the adult rat brain. Phil Trans Res Soc Lond. 1994;B:175–221. - PubMed
-
- Li ZS, Furness JB. Nitric oxide synthase in the enteric nervous system of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Arch Histol Cytol. 1993;36:185–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

