Smc5p promotes faithful chromosome transmission and DNA repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 16452135
- PMCID: PMC1456416
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.053876
Smc5p promotes faithful chromosome transmission and DNA repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
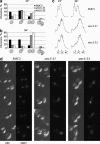
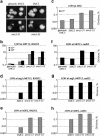
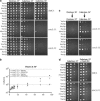
Heterodimers of structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins form the core of several protein complexes involved in the organization of DNA, including condensation and cohesion of the chromosomes at metaphase. The functions of the complexes with a heterodimer of Smc5p and Smc6p are less clear. To better understand them, we created two S. cerevisiae strains bearing temperature-sensitive alleles of SMC5. When shifted to the restrictive temperature, both mutants lose viability gradually, concomitant with the appearance of nuclear abnormalities and phosphorylation of the Rad53p DNA damage checkpoint protein. Removal of Rad52p or overexpression of the SUMO ligase Mms21p partially suppresses the temperature sensitivity of smc5 strains and increases their survival at the restrictive temperature. At the permissive temperature, smc5-31 but not smc5-33 cells exhibit hypersensitivity to several DNA-damaging agents despite induction of the DNA damage checkpoint. Similarly, smc5-31 but not smc5-33 cells are killed by overexpression of the SUMO ligase-defective Mms21-SAp but not by overexpression of wild-type Mms21p. Both smc5 alleles are synthetically lethal with mms21-SA and exhibit Rad52p-independent chromosome fragmentation and loss at semipermissive temperatures. Our data indicate a critical role for the S. cerevisiae Smc5/6-containing complexes in both DNA repair and chromosome segregation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
ATPase-dependent control of the Mms21 SUMO ligase during DNA repair.PLoS Biol. 2015 Mar 12;13(3):e1002089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002089. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2015. PMID: 25764370 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction mapping between Saccharomyces cerevisiae Smc5 and SUMO E3 ligase Mms21.Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 22;50(46):10182-8. doi: 10.1021/bi201376e. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21999667
-
Mec1-dependent phosphorylation of Mms21 modulates its SUMO ligase activity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Apr;28:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Jan 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25659338
-
The Smc5/6 complex: more than repair?Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:179-87. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.047. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21467147 Review.
-
Smc5/6, an atypical SMC complex with two RING-type subunits.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):2159-2171. doi: 10.1042/BST20200389. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32964921 Review.
Cited by
-
Homologous recombination-dependent rescue of deficiency in the structural maintenance of chromosomes (Smc) 5/6 complex.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5119-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.201608. Epub 2010 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21138837 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Sep;76(3):530-64. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05020-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22933559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mdt1 facilitates efficient repair of blocked DNA double-strand breaks and recombinational maintenance of telomeres.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(18):6532-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00471-07. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17636027 Free PMC article.
-
The unnamed complex: what do we know about Smc5-Smc6?Chromosome Res. 2009;17(2):251-63. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-9016-8. Chromosome Res. 2009. PMID: 19308705 Review.
-
Sumoylation and the structural maintenance of chromosomes (Smc) 5/6 complex slow senescence through recombination intermediate resolution.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 16;285(16):11922-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041277. Epub 2010 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20159973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman et al., 2005. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York.
-
- Brachmann, C. B., A. Davies, G. J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li et al., 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14: 115–132. - PubMed
-
- Cha, R. S., and N. Kleckner, 2002. ATR homolog Mec1 promotes fork progression, thus averting breaks in replication slow zones. Science 297: 602–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

