Drusen complement components C3a and C5a promote choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 16452172
- PMCID: PMC1413680
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408835103
Drusen complement components C3a and C5a promote choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
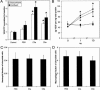
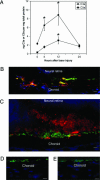
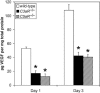
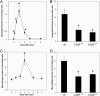
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in industrialized nations, affecting 30-50 million people worldwide. The earliest clinical hallmark of AMD is the presence of drusen, extracellular deposits that accumulate beneath the retinal pigmented epithelium. Although drusen nearly always precede and increase the risk of choroidal neovascularization (CNV), the late vision-threatening stage of AMD, it is unknown whether drusen contribute to the development of CNV. Both in patients with AMD and in a recently described mouse model of AMD, early subretinal pigmented epithelium deposition of complement components C3 and C5 occurs, suggesting a contributing role for these inflammatory proteins in the development of AMD. Here we provide evidence that bioactive fragments of these complement components (C3a and C5a) are present in drusen of patients with AMD, and that C3a and C5a induce VEGF expression in vitro and in vivo. Further, we demonstrate that C3a and C5a are generated early in the course of laser-induced CNV, an accelerated model of neovascular AMD driven by VEGF and recruitment of leukocytes into the choroid. We also show that genetic ablation of receptors for C3a or C5a reduces VEGF expression, leukocyte recruitment, and CNV formation after laser injury, and that antibody-mediated neutralization of C3a or C5a or pharmacological blockade of their receptors also reduces CNV. Collectively, these findings establish a mechanistic basis for the clinical observation that drusen predispose to CNV, revealing a role for immunological phenomena in angiogenesis and providing therapeutic targets for AMD.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.A. is listed on a patent application filed by the University of Kentucky describing these findings.
Figures


References
-
- Smith W., Assink J., Klein R., Mitchell P., Klaver C. C., Klein B. E., Hofman A., Jensen S., Wang J. J., de Jong P. T. Ophthalmology. 2001;108:697–704. - PubMed
-
- Bressler S. B., Maguire M. G., Bressler N. M., Fine S. L. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1990;108:1442–1447. - PubMed
-
- Macular Photocoagulation Study Group. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997;115:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Ambati J., Ambati B. K., Yoo S. H., Ianchulev S., Adamis A. P. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2003;48:257–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- EY14448/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30EY014800/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY14428/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014448/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 GM069736/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015422/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DC000065/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014428/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY15422/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- GM62134/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062134/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32DC00065/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014800/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- GM69736/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

