Beta1 integrin inhibitory antibody induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells, inhibits growth, and distinguishes malignant from normal phenotype in three dimensional cultures and in vivo
- PMID: 16452209
- PMCID: PMC2933188
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3071
Beta1 integrin inhibitory antibody induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells, inhibits growth, and distinguishes malignant from normal phenotype in three dimensional cultures and in vivo
Abstract
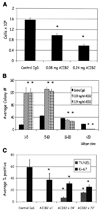
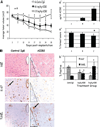
Current therapeutic approaches to cancer are designed to target molecules that contribute to malignant behavior but leave normal tissues intact. beta(1) integrin is a candidate target well known for mediating cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions that influence diverse cellular functions; its aberrant expression has been implicated in breast cancer progression and resistance to cytotoxic therapy. The addition of beta(1) integrin inhibitory agents to breast cancer cells at a single-cell stage in a laminin-rich ECM (three-dimensional lrECM) culture was shown to down-modulate beta(1) integrin signaling, resulting in malignant reversion. To investigate beta(1) integrin as a therapeutic target, we modified the three-dimensional lrECM protocol to approximate the clinical situation: before treatment, we allowed nonmalignant cells to form organized acinar structures and malignant cells to form tumor-like colonies. We then tested the ability of beta(1) integrin inhibitory antibody, AIIB2, to inhibit tumor cell growth in several breast cancer cell lines (T4-2, MDA-MB-231, BT474, SKBR3, and MCF-7) and one nonmalignant cell line (S-1). We show that beta(1) integrin inhibition resulted in a significant loss of cancer cells, associated with a decrease in proliferation and increase in apoptosis, and a global change in the composition of residual colonies. In contrast, nonmalignant cells that formed tissue-like structures remained resistant. Moreover, these cancer cell-specific antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects were confirmed in vivo with no discernible toxicity to animals. Our findings indicate that beta(1) integrin is a promising therapeutic target, and that the three-dimensional lrECM culture assay can be used to effectively distinguish malignant and normal tissue response to therapy.
Figures
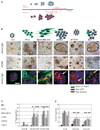
 ) of colonies cultured in three-dimensional lrECM. Phalloidin was used to stain actin filaments (
) of colonies cultured in three-dimensional lrECM. Phalloidin was used to stain actin filaments ( ), and DAPI was used to stain individual nuclei (
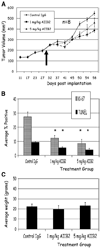
), and DAPI was used to stain individual nuclei ( ). Bar, 13 µm for all cell lines shown. C, whereas there were no significant changes in Ki-67 or TUNEL expressing cells among nonmalignant S-1 cells after β1 integrin inhibition, malignant cell lines, except SKBR3, had a significant decrease in Ki-67 expressing cells and a significant increase in TUNEL-positive cells after antibody treatment. Columns, mean (n = 3); bars, SE. P < 0.05, t test.
). Bar, 13 µm for all cell lines shown. C, whereas there were no significant changes in Ki-67 or TUNEL expressing cells among nonmalignant S-1 cells after β1 integrin inhibition, malignant cell lines, except SKBR3, had a significant decrease in Ki-67 expressing cells and a significant increase in TUNEL-positive cells after antibody treatment. Columns, mean (n = 3); bars, SE. P < 0.05, t test.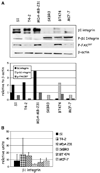
References
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2000;19:6550–6565. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783–792. - PubMed
-
- Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E. Integrin signaling. Science. 1999;285:1028–1032. - PubMed
-
- White DE, Kurpios NA, Zuo D, et al. Targeted disruption of β1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor induction. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:159–170. - PubMed
-
- Berry MG, Gui GP, Wells CA, Carpenter R. Integrin expression and survival in human breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;30:484–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

