The post-translational synthesis of a polyamine-derived amino acid, hypusine, in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A)
- PMID: 16452303
- PMCID: PMC2494880
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvj034
The post-translational synthesis of a polyamine-derived amino acid, hypusine, in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A)
Abstract
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) is the only cellular protein that contains the unique polyamine-derived amino acid, hypusine [Nepsilon-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)lysine]. Hypusine is formed in eIF5A by a novel post-translational modification reaction that involves two enzymatic steps. In the first step, deoxyhypusine synthase catalyzes the cleavage of the polyamine spermidine and transfer of its 4-aminobutyl moiety to the epsilon-amino group of one specific lysine residue of the eIF5A precursor to form a deoxyhypusine intermediate. In the second step, deoxyhypusine hydroxylase converts the deoxyhypusine-containing intermediate to the hypusine-containing mature eIF5A. The structure and mechanism of deoxyhypusine synthase have been extensively characterized. Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase is a HEAT-repeat protein with a symmetrical superhelical structure consisting of 8 helical hairpins (HEAT motifs). It is a novel metalloenzyme containing tightly bound iron at the active sites. Four strictly conserved His-Glu pairs were identified as iron coordination sites. The structural fold of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase is entirely different from those of the other known protein hydroxylases such as prolyl 4-hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylases. The eIF5A protein and deoxyhypusine/hypusine modification are essential for eukaryotic cell proliferation. Thus, hypusine synthesis represents the most specific protein modification known to date, and presents a novel target for intervention in mammalian cell proliferation.
Figures

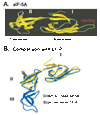

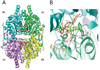

References
-
- Park MH, Lee YB, Joe YA. Hypusine is essential for eukaryotic cell proliferation. Biol. Signals. 1997;6:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Chen KY, Liu AY. Biochemistry and function of hypusine formation on eukaryotic initiation factor 5A. Biol. Signals. 1997;6:105–109. - PubMed
-
- Shiba T, Mizote H, Kaneko T, Nakajima T, Kakimoto Y. Hypusine, a new amino acid occurring in bovine brain. Isolation and structural determination. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1971;244:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

