Positive selection of the Hrp pilin HrpE of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas
- PMID: 16452423
- PMCID: PMC1367247
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.4.1405-1410.2006
Positive selection of the Hrp pilin HrpE of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas
Abstract
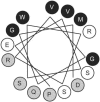
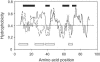
The plant-pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria possesses a type III secretion (TTS) system which is encoded by the 23-kb hrp (hypersensitive response and pathogenicity) gene cluster. The TTS system is necessary for pathogenicity in susceptible hosts and induction of the hypersensitive response in resistant plants. At the cell surface, the TTS system is associated with an extracellular filamentous structure, the Hrp pilus, which serves as a conduit for the transfer of bacterial proteins into the plant cell cytosol. The major pilus component, the HrpE pilin, is unique to xanthomonads. Previous work showed that HrpE contains two regions: a hypervariable surface-exposed domain, including the N-terminal secretion signal, and a C-terminal polymerization domain. In this study, the evolutionary rate of the hrpE gene was analyzed. Twenty-one alleles were cloned, sequenced, and compared with five known hrpE alleles. The ratio of synonymous (K(s)) and nonsynonymous (K(a)) substitution rates shows that parts of the HrpE N terminus are subjected to positive selection and the C terminus is subjected to purifying selection. The trade-off between positive and purifying selection at the very-N terminus allowed us to ascertain the amphipathic alpha-helical nature of the TTS signal. This is the first report of a surface structure from a plant-pathogenic bacterium that evolved under the constraint of positive selection and hints to the evolutionary adaptation of this extracellular appendage to avoid recognition by the plant defense surveillance system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Domain structure of HrpE, the Hrp pilus subunit of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria.J Bacteriol. 2005 Sep;187(17):6175-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.17.6175-6186.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16109959 Free PMC article.
-
The type III-dependent Hrp pilus is required for productive interaction of Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria with pepper host plants.J Bacteriol. 2005 Apr;187(7):2458-68. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.7.2458-2468.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15774889 Free PMC article.
-
Refinement of the Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria hrpD and hrpE operon structure.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007 May;20(5):559-67. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-5-0559. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007. PMID: 17506333
-
HrpE, the major component of the Xanthomonas type three protein secretion pilus, elicits plant immunity responses.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 29;8(1):9842. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27869-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29959345 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the hrp clusters of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola that control the hypersensitive response in nonhost tobacco and pathogenicity in susceptible host rice.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Sep;72(9):6212-24. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00511-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16957248 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Allelic Variation and Selection in Effector Genes of Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary.Pathogens. 2020 Jul 9;9(7):551. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070551. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32659973 Free PMC article.
-
The non-flagellar type III secretion system evolved from the bacterial flagellum and diversified into host-cell adapted systems.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002983. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002983. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028376 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of the bacterial root microbiota in wild and domesticated barley.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Mar 11;17(3):392-403. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 25732064 Free PMC article.
-
The Type III secretion system of Xanthomonas fuscans subsp. fuscans is involved in the phyllosphere colonization process and in transmission to seeds of susceptible beans.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 May;74(9):2669-78. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02906-07. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18326683 Free PMC article.
-
Commonalities and differences of T3SSs in rhizobia and plant pathogenic bacteria.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 27;5:114. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00114. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24723933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson, D. M., and O. Schneewind. 1997. A mRNA signal for the type III secretion of Yop proteins by Yersinia enterocolitica. Science 278:1140-1143. - PubMed
-
- Bonas, U., R. Schulte, S. Fenselau, G. V. Minsavage, B. J. Staskawicz, and R. E. Stall. 1991. Isolation of a gene cluster from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria that determines pathogenicity and the hypersensitive response on pepper and tomato. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 4:81-88.
-
- Comeron, J. M. 1999. K-Estimator: calculation of the number of nucleotide substitutions per site and the confidence intervals. Bioinformatics 15:763-764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

