Binding of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
- PMID: 16452507
- PMCID: PMC1361706
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1389006
Binding of a novel SMG-1-Upf1-eRF1-eRF3 complex (SURF) to the exon junction complex triggers Upf1 phosphorylation and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
Abstract
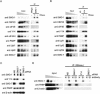
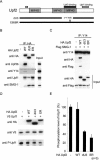
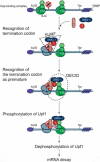
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance mechanism that degrades mRNA containing premature termination codons (PTCs). In mammalian cells, recognition of PTCs requires translation and depends on the presence on the mRNA with the splicing-dependent exon junction complex (EJC). While it is known that a key event in the triggering of NMD is phosphorylation of the trans-acting factor, Upf1, by SMG-1, the relationship between Upf1 phosphorylation and PTC recognition remains undetermined. Here we show that SMG-1 binds to the mRNA-associated components of the EJC, Upf2, Upf3b, eIF4A3, Magoh, and Y14. Further, we describe a novel complex that contains the NMD factors SMG-1 and Upf1, and the translation termination release factors eRF1 and eRF3 (SURF). Importantly, an association between SURF and the EJC is required for SMG-1-mediated Upf1 phosphorylation and NMD. Thus, the SMG-1-mediated phosphorylation of Upf1 occurs on the association of SURF with EJC, which provides the link between the EJC and recognition of PTCs and triggers NMD.
Figures







Comment in
-
Quality control of gene expression: a stepwise assembly pathway for the surveillance complex that triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Genes Dev. 2006 Feb 15;20(4):391-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.1407606. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16481468 Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
