The endocannabinoid system promotes astroglial differentiation by acting on neural progenitor cells
- PMID: 16452678
- PMCID: PMC6675499
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3101-05.2006
The endocannabinoid system promotes astroglial differentiation by acting on neural progenitor cells
Abstract
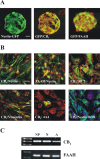
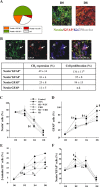
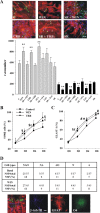
Endocannabinoids exert an important neuromodulatory role via presynaptic cannabinoid CB1 receptors and may also participate in the control of neural cell death and survival. The function of the endocannabinoid system has been extensively studied in differentiated neurons, but its potential role in neural progenitor cells remains to be elucidated. Here we show that the CB1 receptor and the endocannabinoid-inactivating enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase are expressed, both in vitro and in vivo, in postnatal radial glia (RC2+ cells) and in adult nestin type I (nestin(+)GFAP+) neural progenitor cells. Cell culture experiments show that CB1 receptor activation increases progenitor proliferation and differentiation into astroglial cells in vitro. In vivo analysis evidences that, in postnatal CB1(-/-) mouse brain, progenitor proliferation and astrogliogenesis are impaired. Likewise, in adult CB1-deficient mice, neural progenitor proliferation is decreased but is increased in fatty acid amide hydrolase-deficient mice. In addition, endocannabinoid signaling controls neural progenitor differentiation in the adult brain by promoting astroglial differentiation of newly born cells. These results show a novel physiological role of endocannabinoids, which constitute a new family of signaling cues involved in the regulation of neural progenitor cell function.
Figures





References
-
- Aguado T, Monory K, Palazuelos J, Stella N, Cravatt B, Lutz B, Marsicano G, Kokaia Z, Guzmán M, Galve-Roperh I (2005). The endocannabinoid system drives neural progenitor proliferation. FASEB J 19:1704–1706. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim D (2004). For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron 41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1999). Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 97:703–716. - PubMed
-
- Egertova M, Cravatt BF, Elphick MR (2003). Comparative analysis of fatty acid amide hydrolase and cb(1) cannabinoid receptor expression in the mouse brain: evidence of a widespread role for fatty acid amide hydrolase in regulation of endocannabinoid signaling. Neuroscience 119:481–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
