Hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors are crucial for adaptive timing of trace eyeblink conditioned response
- PMID: 16452679
- PMCID: PMC6675508
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4142-05.2006
Hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors are crucial for adaptive timing of trace eyeblink conditioned response
Abstract
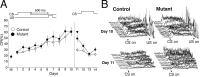
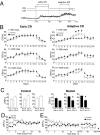
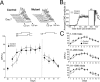
Classical conditioning of the eyeblink reflex is a simple form of associative learning for motor responses. To examine the involvement of hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors (NRs) in nonspatial associative memory, mice lacking an NR1 subunit selectively in adult CA3 pyramidal cells [CA3-NR1 knock-out (KO) mice] were subjected to eyeblink conditioning paradigms. Mice received paired presentations of an auditory conditioned stimulus (CS) and a periorbital shock unconditioned stimulus (US). With repeated presentation of the CS followed by the US, wild-type mice learned to blink in anticipation of the US before its onset. We first confirmed that wild-type mice require an intact hippocampus in the trace version of eyeblink conditioning in which the CS and US do not overlap, creating a stimulus-free time gap of 500 ms. Under the same condition, CA3-NR1 KO mice successfully acquired conditioned responses (CRs) during the 10 d acquisition sessions, whereas the extinction of CRs was impaired on the first day of extinction sessions. Importantly, CA3-NR1 KO mice were impaired in the formation of an adaptively timed CR during the first five trials in the daily acquisition sessions. The aberrantly timed CR was also observed in the extinction sessions in accordance with the impaired extinction of CRs. These results indicate that CA3-NR1 KO mice are unable to rapidly retrieve adaptive CR timing, suggesting that CA3 NRs play a crucial role in the memory of adaptive CR timing in trace conditioning.
Figures



References
-
- Abbott LF, Blum KI (1996). Functional significance of long-term potentiation for sequence learning and prediction. Cereb Cortex 6:406–416. - PubMed
-
- August DA, Levy WB (1999). Temporal sequence compression by an integrate-and-fire model of hippocampal area CA3. J Comput Neurosci 6:71–90. - PubMed
-
- Chan KH, Morell JR, Jarrard LE, Davidson TL (2001). Reconsideration of the role of the hippocampus in learned inhibition. Behav Brain Res 119:111–130. - PubMed
-
- Cho YH, Friedman E, Silva AJ (1999). Ibotanate lesions of the hippocampus impair spatial learning but not contextual fear conditioning in mice. Behav Brain Res 98:77–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
