Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 16453027
- PMCID: PMC1359059
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26679
Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
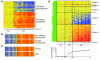
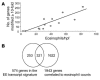
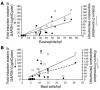
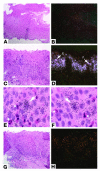
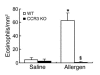
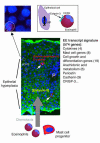
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) is an emerging disorder with a poorly understood pathogenesis. In order to define disease mechanisms, we took an empirical approach analyzing esophageal tissue by a genome-wide microarray expression analysis. EE patients had a striking transcript signature involving 1% of the human genome that was remarkably conserved across sex, age, and allergic status and was distinct from that associated with non-EE chronic esophagitis. Notably, the gene encoding the eosinophil-specific chemoattractant eotaxin-3 (also known as CCL26) was the most highly induced gene in EE patients compared with its expression level in healthy individuals. Esophageal eotaxin-3 mRNA and protein levels strongly correlated with tissue eosinophilia and mastocytosis. Furthermore, a single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human eotaxin-3 gene was associated with disease susceptibility. Finally, mice deficient in the eotaxin receptor (also known as CCR3) were protected from experimental EE. These results implicate eotaxin-3 as a critical effector molecule for EE and provide insight into disease pathogenesis.
Figures




Comment in
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: new insights into an emerging disease.Gastroenterology. 2006 Dec;131(6):2018-20; discussion 2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.10.058. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 17188967 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fox VL, Nurko S, Furuta GT. Eosinophilic esophagitis: it’s not just kid’s stuff. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002;56:260–270. - PubMed
-
- Straumann A, et al. Natural history of primary eosinophilic esophagitis: a follow-up of 30 adult patients for up to 11.5 years. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1660–1669. - PubMed
-
- Orenstein SR, et al. The spectrum of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis beyond infancy: a clinical series of 30 children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000;95:1422–1430. - PubMed
-
- Cheung KM, Oliver MR, Cameron DJ, Catto-Smith AG, Chow CW. Esophageal eosinophilia in children with dysphagia. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003;37:498–503. - PubMed
-
- Noel RJ, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;351:940–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

