Homocysteine transport by human aortic endothelial cells: identification and properties of import systems
- PMID: 16455044
- PMCID: PMC2846170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2005.12.014
Homocysteine transport by human aortic endothelial cells: identification and properties of import systems
Abstract
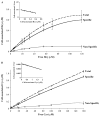
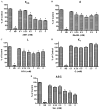
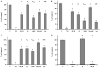
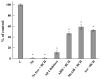
Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Transport of L-homocysteine into and out of the human vascular endothelium is poorly understood. We hypothesized that cultured human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) would import L-homocysteine on one or more of the L-cysteine transport systems. Inhibitors of the transporters were used to characterize the uptake of [35S]L-homocysteine, [35S]L-homocystine, and [35S]L-cysteine. We found that L-homocysteine uptake is mediated by the sodium-dependent cysteine transport systems X(AG), ASC, and A, and the sodium-independent transport system L. Thus, HAEC utilize multiple cysteine transporters (X(AG) > or = L > ASC > A) to import L-homocysteine. Kinetic analysis supported the uptake results. Michaelis-Menten constants (Km) for the four systems yielded values of 19.0, 27.1, 112, and 1000 microM for systems L, X(AG), ASC, and A, respectively. The binding and uptake of [35S]L-homocystine, the disulfide homodimer of L-homocysteine, was mediated by systems X(AG), L, and ASC but not by system A. In contrast to [35S]L-homocysteine, system x(c) was active for [35S]L-homocystine uptake. A similar pattern was observed for [35S]L-cysteine. Thus, L-homocysteine and L-homocystine found in hyperhomocysteinemic subjects can gain entry into the vascular endothelium by way of multiple L-cysteine transporters.
Figures

References
-
- Carmel R, Jacobsen DW. Homocysteine in Health and Disease. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2001.
-
- Clarke R, Smith AD, Jobst KA, Refsum H, Sutton L, Ueland PM. Arch Neurol. 1998;55:1449–1455. - PubMed
-
- Seshadri S, Beiser A, Selhub J, Jacques PF, Rosenberg IH, D’Agostino RB, Wilson PWF, Wolf PA. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:476–483. - PubMed
-
- Vollset SE, Refsum H, Irgens LM, Emblem BM, Tverdal A, Gjessing HK, Monsen ALB, Ueland PM. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:962–968. - PubMed
-
- Murphy MM, Scott JM, Arija V, Molloy AM, Fernandez-Ballart JD. Clin Chem. 2004;50:1406–1412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

