Anthrax lethal factor and edema factor act on conserved targets in Drosophila
- PMID: 16455799
- PMCID: PMC1413899
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0510748103
Anthrax lethal factor and edema factor act on conserved targets in Drosophila
Abstract
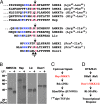
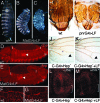
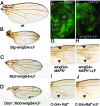
Many bacterial toxins act on conserved components of essential host-signaling pathways. One consequence of this conservation is that genetic model organisms such as Drosophila melanogaster can be used for analyzing the mechanism of toxin action. In this study, we characterize the activities of two anthrax virulence factors, lethal factor (LF) and edema factor, in transgenic Drosophila. LF is a zinc metalloprotease that cleaves and inactivates most human mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinases (MAPKKs). We found that LF similarly cleaves the Drosophila MAPK kinases Hemipterous (Hep) and Licorne in vitro. Consistent with these observations, expression of LF in Drosophila inhibited the Hep/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway during embryonic dorsal closure and the related process of adult thoracic closure. Epistasis experiments confirmed that LF acts at the level of Hep. We also found that LF inhibits Ras/MAPK signaling during wing development and that LF acts upstream of MAPK and downstream of Raf, consistent with LF acting at the level of Dsor. In addition, we found that edema factor, a potent adenylate cyclase, inhibits the hh pathway during wing development, consistent with the known role of cAMP-dependent PKA in suppressing the Hedgehog response. These results demonstrate that anthrax toxins function in Drosophila as they do in mammalian cells and open the way to using Drosophila as a multicellular host system for studying the in vivo function of diverse toxins and virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: E.B. holds shares in NovaScape Sciences.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fighting anthrax with flies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 28;103(9):3013-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600477103. Epub 2006 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16492749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bier E. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005;6:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Bier E., McGinnis W. In: Molecular Basis of Inborn Errors of Development. Epstein C. J., Erikson R. P., Wynshaw-Boris A., editors. New York: Oxford Univ. Press; 2004. pp. 25–45.
-
- Beutler B. Mol. Immunol. 2004;40:845–859. - PubMed
-
- Collier R. J., Young J. A. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003;19:45–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

