Evaluation of the new GenoType Mycobacterium assay for identification of mycobacterial species
- PMID: 16455880
- PMCID: PMC1392669
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.44.2.334-339.2006
Evaluation of the new GenoType Mycobacterium assay for identification of mycobacterial species
Abstract
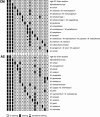
The new commercial assay GenoType Mycobacterium, intended for the identification of mycobacteria, was evaluated with a panel of 197 strains belonging to 86 different taxa. The system, which relies on solid-phase reverse hybridization, is composed of two different kits: GenoType CM for the identification of more frequently detected mycobacterial species and GenoType AS for less common species. The sensitivity and specificity were 97.9% and 92.4% for the CM kit and 99.3% and 99.4% for the AS kit. Our results show that the system may represent a useful tool to substantially enlarge the number of mycobacteria that can be reliably identified in clinical laboratories.
Figures
References
-
- Alcaide, F., I. Richter, C. Bernasconi, B. Springer, C. Hagenau, R. Schulze-Röbbecke, E. Tortoli, R. Martín, E. Böttger, and A. Telenti. 1997. Heterogeneity and clonality among isolates of Mycobacterium kansasii: implications for epidemiological and pathogenicity studies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:1959-1964. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials