Proximal region of the gene encoding cytadherence-related protein permits molecular typing of Mycoplasma genitalium clinical strains by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- PMID: 16455921
- PMCID: PMC1392663
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.44.2.598-603.2006
Proximal region of the gene encoding cytadherence-related protein permits molecular typing of Mycoplasma genitalium clinical strains by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism
Abstract
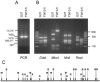
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of the PCR-amplified proximal region of the gene encoding cytadherence accessory protein P110 (MG192) revealed DNA sequence divergences among 54 Mycoplasma genitalium clinical strains isolated from the genitourinary tracts of women attending a sexually transmitted disease-related health clinic, plus one from the respiratory tract and one from synovial fluid. Seven of 56 (12.5%) strains exhibited RFLPs following digestion of the proximal region with restriction endonuclease MboI or RsaI, or both. No sequence variability was detected in the distal portion of the gene.
Figures



References
-
- Barbeyrac, B., C. Bernet-Poggi, F. Febrer, H. Renaudin, M. Dupon, and C. Bebear. 1993. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma genitalium in clinical samples by polymerase chain reaction. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17:S83-S89. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard, A., W. Hamrick, L. Duffy, K. Baldus, and G. H. Cassell. 1993. Use of the polymerase chain reaction for detection of Mycoplasma fermentans and Mycoplasma genitalium in the urogenital tract and amniotic fluid. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17(Suppl. 1):S272-S279. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

