Molecular dynamics simulations of sarcin-ricin rRNA motif
- PMID: 16456030
- PMCID: PMC1360246
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkj470
Molecular dynamics simulations of sarcin-ricin rRNA motif
Abstract
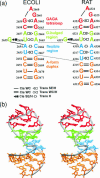
Explicit solvent molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were carried out for sarcin-ricin domain (SRD) motifs from 23S (Escherichia coli) and 28S (rat) rRNAs. The SRD motif consists of GAGA tetraloop, G-bulged cross-strand A-stack, flexible region and duplex part. Detailed analysis of the overall dynamics, base pairing, hydration, cation binding and other SRD features is presented. The SRD is surprisingly static in multiple 25 ns long simulations and lacks any non-local motions, with root mean square deviation (r.m.s.d.) values between averaged MD and high-resolution X-ray structures of 1-1.4 A. Modest dynamics is observed in the tetraloop, namely, rotation of adenine in its apex and subtle reversible shift of the tetraloop with respect to the adjacent base pair. The deformed flexible region in low-resolution rat X-ray structure is repaired by simulations. The simulations reveal few backbone flips, which do not affect positions of bases and do not indicate a force field imbalance. Non-Watson-Crick base pairs are rigid and mediated by long-residency water molecules while there are several modest cation-binding sites around SRD. In summary, SRD is an unusually stiff rRNA building block. Its intrinsic structural and dynamical signatures seen in simulations are strikingly distinct from other rRNA motifs such as Loop E and Kink-turns.
Figures



References
-
- Hausner T.P., Atmadja J., Nierhaus K.H. Evidence that the G2661 region of 23S ribosomal-RNA is located at the ribosomal-binding sites of both elongation-factors. Biochimie. 1987;69:911–923. - PubMed
-
- Moazed D., Robertson J.M., Noller H.F. Interaction of elongation-factors Ef-G and Ef-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988;334:362–364. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y., Wool I.G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes—the sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S-ribosomal ribonucleic-acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1982;257:9054–9060. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes—the site and the characteristics of the modification in 28-S ribosomal-RNA caused by the toxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:5908–5912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

