Molecular analysis of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase mu-mediated cell adhesion
- PMID: 16456543
- PMCID: PMC1383555
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600974
Molecular analysis of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase mu-mediated cell adhesion
Abstract
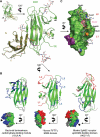
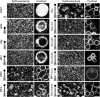
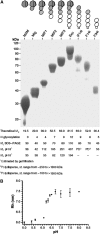
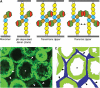
Type IIB receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are bi-functional cell surface molecules. Their ectodomains mediate stable, homophilic, cell-adhesive interactions, whereas the intracellular catalytic regions can modulate the phosphorylation state of cadherin/catenin complexes. We describe a systematic investigation of the cell-adhesive properties of the extracellular region of RPTPmu, a prototypical type IIB RPTP. The crystal structure of a construct comprising its N-terminal MAM (meprin/A5/mu) and Ig domains was determined at 2.7 A resolution; this assigns the MAM fold to the jelly-roll family and reveals extensive interactions between the two domains, which form a rigid structural unit. Structure-based site-directed mutagenesis, serial domain deletions and cell-adhesion assays allowed us to identify the four N-terminal domains (MAM, Ig, fibronectin type III (FNIII)-1 and FNIII-2) as a minimal functional unit. Biophysical characterization revealed at least two independent types of homophilic interaction which, taken together, suggest that there is the potential for formation of a complex and possibly ordered array of receptor molecules at cell contact sites.
Figures

References
-
- Aricescu AR, Fulga TA, Cismasiu V, Goody RS, Szedlacsek SE (2001) Intramolecular interactions in protein tyrosine phosphatase RPTPmu: kinetic evidence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280: 319–327 - PubMed
-
- Beckmann G, Bork P (1993) An adhesive domain detected in functionally diverse receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 18: 40–41 - PubMed
-
- Beltran PJ, Bixby JL (2003) Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases as mediators of cellular adhesion. Front Biosci 8: d87–d99 - PubMed
-
- Bianchi C, Sellke FW, Del Vecchio RL, Tonks NK, Neel BG (1999) Receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase mu is expressed in specific vascular endothelial beds in vivo. Exp Cell Res 248: 329–338 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

