Cyclic stretch attenuates effects of hyperoxia on cell proliferation and viability in human alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 16461433
- PMCID: PMC2683386
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00160.2005
Cyclic stretch attenuates effects of hyperoxia on cell proliferation and viability in human alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
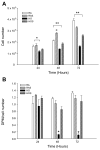
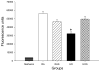
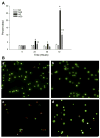
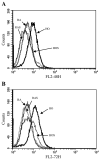
The treatment of severe lung disease often requires the use of high concentrations of oxygen coupled with the need for assisted ventilation, potentially exposing the pulmonary epithelium to both reactive oxygen species and nonphysiological cyclic stretch. Whereas prolonged hyperoxia is known to cause increased cell injury, cyclic stretch may result in either cell proliferation or injury depending on the pattern and degree of exposure to mechanical deformation. How hyperoxia and cyclic stretch interact to affect the pulmonary epithelium in vitro has not been previously investigated. This study was performed using human alveolar epithelial A549 cells to explore the combined effects of cyclic stretch and hyperoxia on cell proliferation and viability. Under room air conditions, cyclic stretch did not alter cell viability at any time point and increased cell number after 48 h compared with unstretched controls. After exposure to prolonged hyperoxia, cell number and [(3)H]thymidine incorporation markedly decreased, whereas evidence of oxidative stress and nonapoptotic cell death increased. The combination of cyclic stretch with hyperoxia significantly mitigated the negative effects of prolonged hyperoxia alone on measures of cell proliferation and viability. In addition, cyclic stretch resulted in decreased levels of oxidative stress over time in hyperoxia-exposed cells. Our results suggest that cyclic stretch, as applied in this study, can minimize the detrimental effects of hyperoxia on alveolar epithelial A549 cells.
Figures




References
-
- Allen RG, Tresini M. Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28:463–499. - PubMed
-
- Cavanaugh KJ, Jr, Margulies SS. Measurement of stretch-induced loss of alveolar epithelial barrier integrity with a novel in vitro method. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283:C1801–C1808. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Chess PR, Toia L, Finkelstein JN. Mechanical strain-induced proliferation and signaling in pulmonary epithelial H441 cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279:L43–L51. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos CC, Slutsky AS. Mechanisms of ventilator-induced lung injury: a perspective. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89:1645–1655. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

