Enumeration and immunohistochemical characterisation of bone marrow basophils in myeloproliferative disorders using the basophil specific monoclonal antibody 2D7
- PMID: 16461568
- PMCID: PMC1860377
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2005.029215
Enumeration and immunohistochemical characterisation of bone marrow basophils in myeloproliferative disorders using the basophil specific monoclonal antibody 2D7
Abstract
Background: Basophils are highly specialised granulocytes that express a unique profile of antigens and increase in myeloproliferative disorders (MPD). In chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML), basophilia is a diagnostic and prognostic determinant. So far, however, no reliable approach for routine detection and enumeration of bone marrow basophils has become available.
Objective: To detect and enumerate basophils in bone marrow sections in patients with CML and other MPD.
Methods: The anti-basophil antibody 2D7 was applied to paraffin embedded bone marrow sections from normal/reactive subjects (n = 31), patients with CML (chronic phase, n = 37; accelerated phase, n = 9), and other MPD (chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (CIMF), n = 20; polycythaemia vera (PV), n = 20; essential thrombocythaemia (ET), n = 20; indolent systemic mastocytosis (ISM), n = 7).
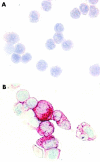
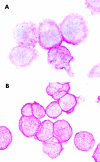
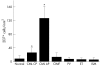
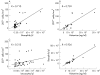
Results: As assessed by serial section staining, 2D7(+) cells were found to co-express myeloperoxidase, histidine decarboxylase, CD9, and CD43, but did not express B cell or T cell restricted antigens. 2D7(+) bone marrow cells were found to increase in CML compared with normal/reactive bone marrow and other MPD (median numbers of 2D7(+) cells/mm(2): CML, 33; normal/reactive bone marrow, 6; CIMF, 10; PV, 6; ET, 5; ISM, 3; p<0.05). The highest basophil counts were recorded in accelerated phase CML (115/mm(2)).
Conclusions: A novel immunohistochemical procedure has been established for basophil detection in normal bone marrow and MPD. This approach should help in the quantification of bone marrow basophils at diagnosis and during anti-leukaemic treatment.
References
-
- Valent P, Bettelheim P. The human basophil. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 199010327–352. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak A M. Cell biology of the basophil. Int Rev Cytol 199818087–236. - PubMed
-
- Falcone F H, Haas H, Gibbs B F. The human basophil: a new appreciation of its role in immune responses. Blood 2000964028–4038. - PubMed
-
- Schroeder J T, MacGlashan D W, Lichtenstein L M. Human basophils: mediator release and cytokine production. Adv Immunol 20017793–122. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak A M. Histamine content and secretion in basophils and mast cells. Prog Histochem Cytochem 199833169–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials