Reliable and rapid identification of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria species by artificial neural network-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 16461640
- PMCID: PMC1392910
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.994-1000.2006
Reliable and rapid identification of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria species by artificial neural network-based Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
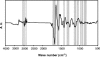
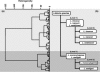
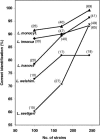
Differentiation of the species within the genus Listeria is important for the food industry but only a few reliable methods are available so far. While a number of studies have used Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to identify bacteria, the extraction of complex pattern information from the infrared spectra remains difficult. Here, we apply artificial neural network technology (ANN), which is an advanced multivariate data-processing method of pattern analysis, to identify Listeria infrared spectra at the species level. A hierarchical classification system based on ANN analysis for Listeria FTIR spectra was created, based on a comprehensive reference spectral database including 243 well-defined reference strains of Listeria monocytogenes, L. innocua, L. ivanovii, L. seeligeri, and L. welshimeri. In parallel, a univariate FTIR identification model was developed. To evaluate the potentials of these models, a set of 277 isolates of diverse geographical origins, but not included in the reference database, were assembled and used as an independent external validation for species discrimination. Univariate FTIR analysis allowed the correct identification of 85.2% of all strains and of 93% of the L. monocytogenes strains. ANN-based analysis enhanced differentiation success to 96% for all Listeria species, including a success rate of 99.2% for correct L. monocytogenes identification. The identity of the 277-strain test set was also determined with the standard phenotypical API Listeria system. This kit was able to identify 88% of the test isolates and 93% of L. monocytogenes strains. These results demonstrate the high reliability and strong potential of ANN-based FTIR spectrum analysis for identification of the five Listeria species under investigation. Starting from a pure culture, this technique allows the cost-efficient and rapid identification of Listeria species within 25 h and is suitable for use in a routine food microbiological laboratory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differentiation of Listeria monocytogenes serovars by using artificial neural network analysis of Fourier-transformed infrared spectra.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Feb;73(3):1036-40. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02004-06. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17142376 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of five Listeria species based on infrared spectra (FTIR) using macrosamples is superior to a microsample approach.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008 Mar;390(6):1629-35. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-1834-1. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18231779
-
Differentiation of different mixed Listeria strains and also acid-injured, heat-injured, and repaired cells of Listeria monocytogenes using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.J Food Prot. 2015 Mar;78(3):540-8. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-160. J Food Prot. 2015. PMID: 25719878
-
Methods for the isolation and identification of Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes: a review.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005 Nov;29(5):851-75. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.002. Epub 2004 Dec 22. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16219509 Review.
-
[Taxonomy of the Listeria genus and typing of L. monocytogenes].Pathol Biol (Paris). 1996 Nov;44(9):749-56. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1996. PMID: 8977897 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Perspectives of FTIR as Promising Tool for Pathogen Diagnosis, Sanitary and Welfare Monitoring in Animal Experimentation Models: A Review Based on Pertinent Literature.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 20;12(4):833. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040833. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection and Identification of Bacillus cereus, Bacillus cytotoxicus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus weihenstephanensis via Machine Learning Based FTIR Spectroscopy.Front Microbiol. 2019 Apr 26;10:902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00902. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31105681 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Listeria monocytogenes serovars by using artificial neural network analysis of Fourier-transformed infrared spectra.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Feb;73(3):1036-40. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02004-06. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17142376 Free PMC article.
-
Quick Detection of Proteus and Pseudomonas in Patients' Urine and Assessing Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Using Infrared Spectroscopy and Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;23(19):8132. doi: 10.3390/s23198132. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37836961 Free PMC article.
-
Direct determination of phosphatase activity from physiological substrates in cells.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0120087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120087. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25785438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allerberger, F., M. Dierich, G. Petranyi, M. Lalic, and A. Bubert. 1997. Nonhemolytic strains of Listeria monocytogenes detected in milk products using VIDAS immunoassay kit. Zentralbl. Hyg. Umweltmed. 200:189-195. - PubMed
-
- American College of Physicians. 2005. Sensitivity, specificity definition. [Online.] http://www.acponline.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

