Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid in top- and subsoil is quantitatively linked to the class III tfdA gene
- PMID: 16461702
- PMCID: PMC1392919
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1476-1486.2006
Degradation of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid in top- and subsoil is quantitatively linked to the class III tfdA gene
Erratum in
- Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 May;72(5):3803
Abstract
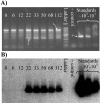
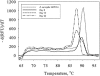
The tfdA gene is known to be involved in the first step of the degradation of the phenoxy acid herbicide 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetic acid (MCPA) in several soil bacteria, but bacteria containing other tfdA-like genes have been isolated as well. A quantitative real-time PCR method was used to monitor the increase in the concentration of tfdA genes during degradation of MCPA in sandy topsoil and subsoil over a period of 115 days. Quantitative PCR revealed growth in the tfdA-containing bacterial community, from 500 genes g(-1) soil to approximately 3 x 10(4) genes g(-1) soil and to 7 x 10(5) genes g(-1) soil for topsoil initially added to 2.3 mg MCPA kg(-1) (dry weight) soil and 20 mg MCPA kg(-1) (dry weight) soil, respectively. We analyzed the diversity of the tfdA gene during the degradation experiment. Analyses of melting curves of real-time PCR amplification products showed that a shift in the dominant tfdA population structure occurred during the degradation period. Further denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequence analysis revealed that the tfdA genes responsible for the degradation of MCPA belonged to the class III tfdA genes, while the tfdA genes present in the soil before the occurrence of degradation belonged to the class I tfdA genes. The implications of these results is that the initial assessment of functional genes in soils does not necessarily reflect the organisms or genes that would carry out the degradation of the compounds in question.
Figures
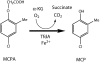





References
-
- Acea, M. J., and M. Alexander. 1988. Growth and survival of bacteria introduced into carbon amended soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 20:703-709.
-
- Acea, M. J., C. R. Moore, and M. Alexander. 1988. Survival and growth of bacteria introduced into soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 20:509-515.
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, S. M., P. B. Hertz, T. Holst, R. Bossi, and C. S. Jacobsen. 2001. Mineralization studies of 14C-labelled metsulfuron-methyl, tribenuron-methyl, chlorsulfuron and thifensulfuron-methyl in one Danish soil and groundwater sediment profile. Chemosphere 45:775-782. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

