Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenases from Ketogulonicigenium vulgare catalyze the direct conversion of L-sorbosone to L-ascorbic acid
- PMID: 16461703
- PMCID: PMC1392885
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1487-1495.2006
Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenases from Ketogulonicigenium vulgare catalyze the direct conversion of L-sorbosone to L-ascorbic acid
Abstract
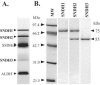
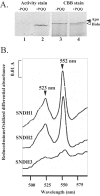
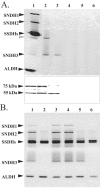
A novel enzyme, L-sorbosone dehydrogenase 1 (SNDH1), which directly converts L-sorbosone to L-ascorbic acid (L-AA), was isolated from Ketogulonicigenium vulgare DSM 4025 and characterized. This enzyme was a homooligomer of 75-kDa subunits containing pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) and heme c as the prosthetic groups. Two isozymes of SNDH, SNDH2 consisting of 75-kDa and 55-kDa subunits and SNDH3 consisting of 55-kDa subunits, were also purified from the bacterium. All of the SNDHs produced L-AA, as well as 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2KGA), from L-sorbosone, suggesting that tautomerization of L-sorbosone causes the dual conversion by SNDHs. The sndH gene coding for SNDH1 was isolated and analyzed. The N-terminal four-fifths of the SNDH amino acid sequence exhibited 40% identity to the sequence of a soluble quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. The C-terminal one-fifth of the sequence exhibited similarity to a c-type cytochrome with a heme-binding motif. A lysate of Escherichia coli cells expressing sndH exhibited SNDH activity in the presence of PQQ and CaCl2. Gene disruption analysis of K. vulgare indicated that all of the SNDH proteins are encoded by the sndH gene. The 55-kDa subunit was derived from the 75-kDa subunit, as indicated by cleavage of the C-terminal domain in the bacterial cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of a group of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenases that are involved in the conversion of L-sorbose to 2-Keto-L-gulonic acid in Ketogulonicigenium vulgare WSH-001.Biotechnol Prog. 2013 Nov-Dec;29(6):1398-404. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1803. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Biotechnol Prog. 2013. PMID: 23970495
-
Systematic characterization of sorbose/sorbosone dehydrogenases and sorbosone dehydrogenases from Ketogulonicigenium vulgare WSH-001.J Biotechnol. 2019 Aug 10;301:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.05.010. Epub 2019 May 25. J Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31136757
-
The membrane-bound sorbosone dehydrogenase of Gluconacetobacter liquefaciens is a pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent enzyme.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020 Jun;137:109511. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109511. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2020. PMID: 32423666
-
[2-KGA metabolism coupling respiratory chain in Ketogulonigenium vulgare--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2014 Oct 4;54(10):1101-8. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 25803886 Review. Chinese.
-
Quinohemoprotein alcohol dehydrogenases: structure, function, and physiology.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004 Aug 1;428(1):10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.03.037. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004. PMID: 15234265 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing an innovative carbohydrate metabolic pathway for efficient production of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid in Ketogulonicigenium robustum initiated by intronic promoters.Microb Cell Fact. 2018 May 19;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12934-018-0932-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2018. PMID: 29778095 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent 2-keto-D-glucose dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas aureofaciens.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(8):1322-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.02376-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645559 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of Ketogulonicigenium vulgare under glutathione reveals high demand for thiamin transport and antioxidant protection.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32156. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032156. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384164 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct promoters affect pyrroloquinoline quinone production in recombinant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae.Curr Microbiol. 2014 Oct;69(4):451-6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-014-0607-7. Epub 2014 May 24. Curr Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24858816
-
Complete genome sequence of the sugarcane nitrogen-fixing endophyte Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus Pal5.BMC Genomics. 2009 Sep 23;10:450. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-450. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19775431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken, A. 1977. Purification and primary structure of cytochrome f from cyanobacterium, Plectonema boryanum. Eur. J. Biochem. 78:273-279. - PubMed
-
- Anthony, C. 1992. The structures of bacterial quinoprotein dehydrogenases. Int. J. Biochem. 24:29-39. - PubMed
-
- Asakura, A., and T. Hoshino. 1999. Isolation and characterization of a new quinoprotein dehydrogenase, l-sorbose/l-sorbosone dehydrogenase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63:46-53. - PubMed
-
- Bleeg, H. S. 1966. l-Ascorbic acid in yeast and isolation of l-galactono-gamma-lactone oxidase from the mitochondria. Enzymologia 31:105-112. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

