Cumulative effects of short-term polymetal contamination on soil bacterial community structure
- PMID: 16461728
- PMCID: PMC1392981
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1684-1687.2006
Cumulative effects of short-term polymetal contamination on soil bacterial community structure
Abstract
In this study we evaluated the short-term effects of copper, cadmium, and mercury, added singly or in combination at different doses, on soil bacterial community structure using the bacterial automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis (B-ARISA) fingerprinting technique. Principal-component analysis of B-ARISA profiles allowed us to deduce the following order of impact: (Cu + Cd + Hg) >> Hg > or = Cd > Cu. These results demonstrated that there was a cumulative effect of metal toxicity. Furthermore, the trend of modifications was consistent with the "hump-backed" relationships between biological diversity and disturbance described by Giller et al. (K. E. Giller, E. Witler, and S. P. McGrath, Soil Biol. Biochem. 30:1389-1414, 1998).
Figures
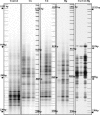

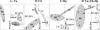

Similar articles
-
Field and microcosm experiments to evaluate the effects of agricultural Cu treatment on the density and genetic structure of microbial communities in two different soils.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2006 Nov;58(2):303-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00157.x. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2006. PMID: 17064271
-
Sequencing bands of ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints for characterization and microscale distribution of soil bacterium populations responding to mercury spiking.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Dec;66(12):5334-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.12.5334-5339.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11097911 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two fingerprinting techniques, terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism and automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis, for determination of bacterial diversity in aquatic environments.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Sep;72(9):5982-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01361-06. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16957219 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of bacterial and fungal soil communities by automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints: biological and methodological variability.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Oct;67(10):4479-87. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.10.4479-4487.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11571146 Free PMC article.
-
Structural diversity of microorganisms in chemically perturbed soil assessed by molecular and cytochemical approaches.J Microbiol Methods. 2001 Jan;43(3):197-212. doi: 10.1016/s0167-7012(00)00197-4. J Microbiol Methods. 2001. PMID: 11118654 Review.
Cited by
-
Stochastically reduced communities-Microfluidic compartments as model and investigation tool for soil microorganism growth in structured spaces.Eng Life Sci. 2017 Apr 18;17(7):792-800. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201600264. eCollection 2017 Jul. Eng Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 32624825 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of mercury in earthworms and the effect of mercury on the associated bacterial communities.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061215. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577209 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic microbial community profiling: a critical technical review.Microb Ecol. 2007 Aug;54(2):276-89. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9199-5. Epub 2007 Mar 8. Microb Ecol. 2007. PMID: 17345133 Review.
-
Contamination of soil by copper affects the dynamics, diversity, and activity of soil bacterial communities involved in wheat decomposition and carbon storage.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Dec;75(23):7565-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00616-09. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19801474 Free PMC article.
-
Bioremediation by Cupriavidus metallidurans Strain MSR33 of Mercury-Polluted Agricultural Soil in a Rotary Drum Bioreactor and Its Effects on Nitrogen Cycle Microorganisms.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 9;8(12):1952. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121952. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33316980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alloway, B. J. 1995. Soil processes and the behaviour of metals, p. 9-38. In B. J. Alloway (ed.), Heavy metals in soils. Chapman and Hall, London, United Kingdom.
-
- Atlas, R. M., A. Horwitz, M. Krichevsky, and A. K. Bej. 1991. Response of microbial populations to environmental disturbance. Microb. Ecol. 22:249-256. - PubMed
-
- Bruins, M. R., S. Kapil, and W. Oehme. 2000. Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 45:198-207. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

