Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition and autoubiquitination by Rabex-5
- PMID: 16462746
- PMCID: PMC1578505
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1064
Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition and autoubiquitination by Rabex-5
Abstract
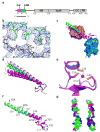
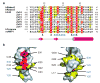
Rabex-5 is an exchange factor for Rab5, a master regulator of endosomal trafficking. Rabex-5 binds monoubiquitin, undergoes covalent ubiquitination and contains an intrinsic ubiquitin ligase activity, all of which require an N-terminal A20 zinc finger followed immediately by a helix. The structure of the N-terminal portion of Rabex-5 bound to ubiquitin at 2.5-A resolution shows that Rabex-5-ubiquitin interactions occur at two sites. The first site is a new type of ubiquitin-binding domain, an inverted ubiquitin-interacting motif, which binds with approximately 29-microM affinity to the canonical Ile44 hydrophobic patch on ubiquitin. The second is a diaromatic patch on the A20 zinc finger, which binds with approximately 22-microM affinity to a polar region centered on Asp58 of ubiquitin. The A20 zinc-finger diaromatic patch mediates ubiquitin-ligase activity by directly recruiting a ubiquitin-loaded ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme.
Figures





Comment in
-
Two new structures of Ub-receptor complexes. U2.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006 Mar;13(3):186-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0306-186. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16518384 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Rab5 guanine nucleotide exchange factor Rabex-5 binds ubiquitin (Ub) and functions as a Ub ligase through an atypical Ub-interacting motif and a zinc finger domain.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 10;281(10):6874-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509939200. Epub 2006 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16407276
-
A new side to ubiquitin.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Oct;31(10):541-4. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.07.009. Epub 2006 Aug 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16901703 Review.
-
Crystal structure of the ubiquitin binding domains of rabex-5 reveals two modes of interaction with ubiquitin.Cell. 2006 Mar 24;124(6):1183-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.020. Epub 2006 Feb 23. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16499958
-
Differential polyubiquitin recognition by tandem ubiquitin binding domains of Rabex-5.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Jul 13;423(4):757-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.06.032. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22705550
-
Ubiquitin-binding domains.Biochem J. 2006 Nov 1;399(3):361-72. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061138. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 17034365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced Purification of Ubiquitinated Proteins by Engineered Tandem Hybrid Ubiquitin-binding Domains (ThUBDs).Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Apr;15(4):1381-96. doi: 10.1074/mcp.o115.051839. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27037361 Free PMC article.
-
Small GTPases of the Rab and Arf Families: Key Regulators of Intracellular Trafficking in Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 23;22(9):4425. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094425. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNF168, a new RING finger, MIU-containing protein that modifies chromatin by ubiquitination of histones H2A and H2AX.BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Jun 5;10:55. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-55. BMC Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19500350 Free PMC article.
-
Coarse-grained models for simulations of multiprotein complexes: application to ubiquitin binding.J Mol Biol. 2008 Feb 1;375(5):1416-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.063. Epub 2007 Nov 28. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18083189 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the Ubp-M BUZ domain, a highly specific protein module that recognizes the C-terminal tail of free ubiquitin.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jul 6;370(2):290-302. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.015. Epub 2007 Apr 12. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17512543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Segev N. Ypt and Rab GTPases: insight into functions through novel interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:500–511. - PubMed
-
- Zerial M, McBride H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Pfeffer S, Aivazian D. Targeting RAB GTPases to distinct membrane compartments. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:886–896. - PubMed
-
- Seabra MC, Wasmeier C. Controlling the location and activation of Rab GTPases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:451–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

