Formation and repair of interstrand cross-links in DNA
- PMID: 16464006
- PMCID: PMC2505341
- DOI: 10.1021/cr040478b
Formation and repair of interstrand cross-links in DNA
Figures


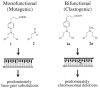
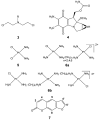
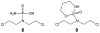
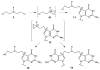






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

